Facing the frustrating message “This PC doesn’t meet the minimum requirements for Windows 11” can be challenging. The upgrade brings many new features, but not every computer is ready for it out of the box. Fortunately, there are ways to fix this issue and upgrade your PC to Windows 11 even if it doesn’t meet the minimum system requirements.
If your computer does not meet the minimum requirements for Windows 11, it may be related to hardware components like the CPU, TPM 2.0, or Secure Boot. These specifications are crucial for security and performance. By adjusting settings or making minor upgrades, you can solve these issues and benefit from the latest OS from Microsoft. Upgrading to Windows 11 can be exciting, but many users encounter the frustrating message “This PC doesn’t meet the minimum requirements for Windows 11.”
This guide will help you understand why you see this message, how to check your system’s compatibility, and potential solutions to get Windows 11 running on your computer. Whether it’s enabling specific features or considering hardware upgrades, we’ll walk you through the steps to overcome this installation hurdle. In some cases, technical workarounds, such as modifying the registry or using third-party tools, can also help bypass these requirements. While these methods are not officially recommended by Microsoft, they have worked for many users.
Troubleshooting Windows 11 Installation Errors
Understanding the Error Message
Seeing the message “This PC doesn’t meet the minimum requirements for Windows 11” means your computer lacks specific hardware or software features Microsoft deems essential for a smooth Windows 11 experience. These include:
| Requirement | Details | How to Check |
|---|---|---|
| Processor | 64-bit processor with 2 or more cores, 1 gigahertz (GHz) or faster clock speed | Open Settings > System > About > Processor |
| RAM | 4 gigabytes (GB) or more | Open Settings > System > About > Installed RAM |
| Storage | 64 GB or larger storage device | Open File Explorer and check the size of your main drive (usually C:) |
| System Firmware | UEFI, Secure Boot capable | Check your motherboard’s documentation or BIOS settings |
| TPM | Trusted Platform Module (TPM) version 2.0 | Search for “tpm.msc” in the Start menu and check the “TPM Specification Version” |
| Graphics Card | Compatible with DirectX 12 or later with WDDM 2.0 driver | Open Device Manager > Display adapters and check the DirectX and WDDM versions of your GPU |
| Display | High definition (720p) display that is greater than 9″ diagonally, 8 bits per color channel | Check your monitor’s specifications |
| Internet Connection | Internet connectivity is required to perform updates and to download and use some features. | Ensure you can access the internet |
How to Fix the Error
- Check for Updates: Ensure your PC’s BIOS and drivers are up-to-date.
- Enable TPM and Secure Boot: These features are often disabled by default in BIOS settings. Refer to your motherboard’s manual for instructions.
- Upgrade Hardware: If your hardware doesn’t meet the requirements, upgrading components like RAM or the graphics card can resolve the issue.
- Bypass the Requirements: There are workarounds to install Windows 11 on unsupported hardware by modifying registry settings, but this isn’t recommended as it could lead to instability.
Use Official Tools to Check Compatibility
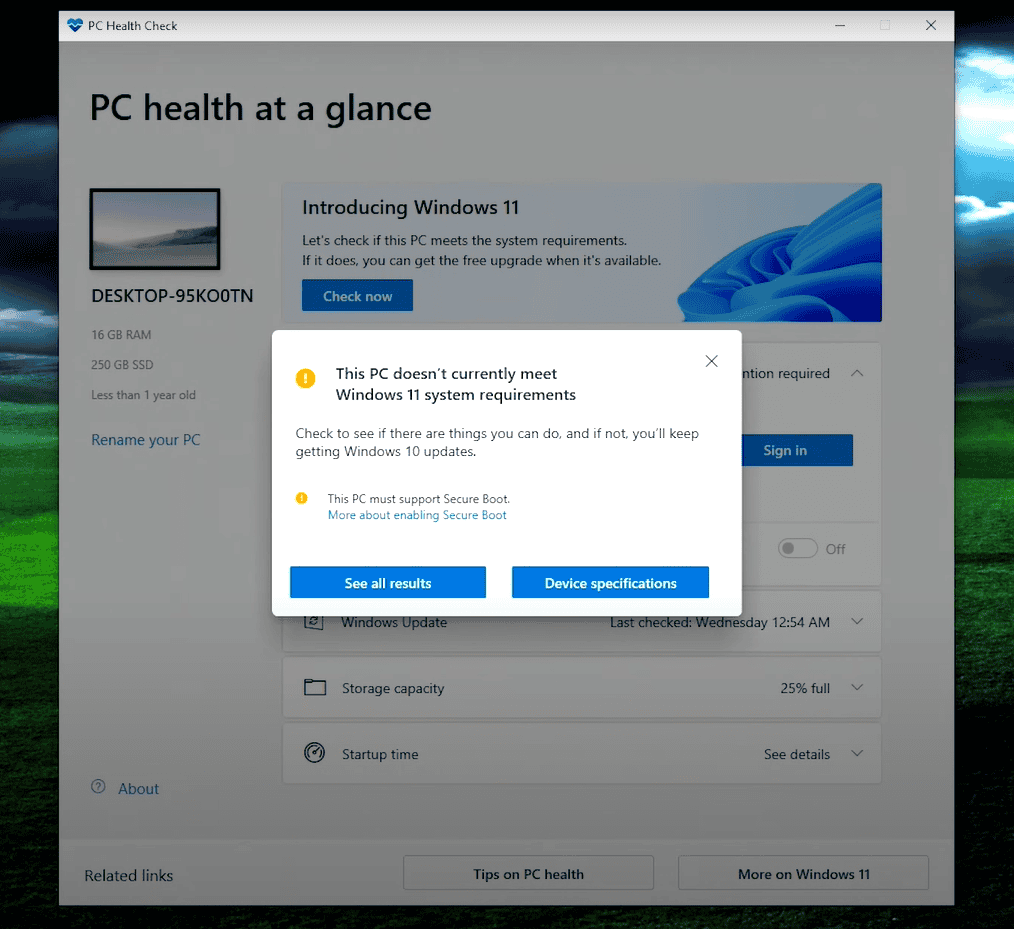
Microsoft provides the PC Health Check app, a free tool that scans your system and provides a detailed report on compatibility with Windows 11. This can help identify which components need an upgrade.
Remember
It’s important to note that bypassing the requirements may lead to issues with updates, security, or functionality. If you’re unable to meet the requirements and have an older device, consider sticking with Windows 10, which will be supported until October 2025.
Key Takeaways
- Fixing the requirements issue often involves changing hardware settings.
- Minor upgrades or tweaks can help bypass the system requirement errors.
- Using unofficial methods can allow Windows 11 installation on unsupported PCs.
Understanding the Minimum System Requirements for Windows 11
Windows 11 has specific hardware requirements that must be met for a successful installation. Understanding these requirements can help you determine if your PC is compatible and troubleshoot any issues.
System Requirements Overview
To run Windows 11, your system must meet a set of minimum hardware requirements. These include the processor, RAM, storage, and security features like TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot. If any of these are missing, your PC may not support the new operating system.
Processor and Memory Specifications
Windows 11 needs a compatible 64-bit processor with at least 1 GHz clock speed and 2 or more cores. Popular CPUs like Intel’s 8th Generation or AMD’s Ryzen 2000 series typically meet these specifications.
RAM is also crucial. Windows 11 requires a minimum of 4 GB. Anything less, and the installation won’t proceed. Ensuring your system meets these criteria helps in avoiding potential issues during installation.
Storage and Graphics
A minimum of 64 GB of storage is needed to install Windows 11. This ensures the OS has enough space alongside essential applications and updates. Hard drives or SSDs can be used as long as they meet the capacity requirement.
Regarding graphics, Windows 11 requires a DirectX 12 compatible GPU with a WDDM 2.0 driver. This ensures smooth performance and visual fidelity. Without a capable graphics system, the installation might fail or the OS may not run correctly.
Security and Firmware
Windows 11 mandates TPM 2.0 support for better security. TPM is a hardware-based security feature used for encryption and secure booting. Secure Boot, part of UEFI firmware, helps prevent unauthorized software from loading during the boot process. These features enhance the security of the operating system.
Secure Boot must be enabled in the UEFI settings. If your motherboard supports UEFI and Secure Boot but it’s not enabled, adjusting these settings in the BIOS can help meet the requirements.
Troubleshooting Incompatible Hardware
If your PC doesn’t meet the requirements, there are a few troubleshooting steps you can take. Use the PC Health Check App to verify compatibility. Sometimes, simple BIOS updates can address compatibility issues.
Disabling legacy boot modes and enabling UEFI and Secure Boot can also help. If TPM support is disabled, it can typically be enabled from the BIOS settings. Addressing each of these areas might resolve the compatibility issues and allow for a successful Windows 11 installation.







