A rapidly draining laptop battery can be frustrating and disruptive. Many users face this issue, wondering why their computer’s power seems to disappear so quickly. The most common causes of fast battery drain include resource-intensive applications, outdated hardware, and poor power settings optimization.
Laptops often struggle with battery life due to the varied hardware ecosystem and less optimization for power efficiency. Windows laptops, in particular, are known for shorter battery life compared to some other systems. This can be exacerbated by running multiple programs simultaneously or using applications that consume a lot of resources.
Battery age also plays a significant role in power drain issues. As batteries get older, they naturally lose capacity and drain faster. Users may need to replace their battery if it’s more than a few years old. Simple adjustments to settings and usage habits can often extend battery life significantly.
What To Do If Your Laptop Battery Is Draining Fast
It’s frustrating when your computer battery dies before you expect it to! Here’s a breakdown of the most common culprits and how to troubleshoot them:
1. Power-Hungry Settings:
- Screen Brightness: This is a major battery drainer.1 Lower your screen brightness to a comfortable level.2
- Keyboard Backlight: If your keyboard is backlit, dim it or turn it off when not needed.3
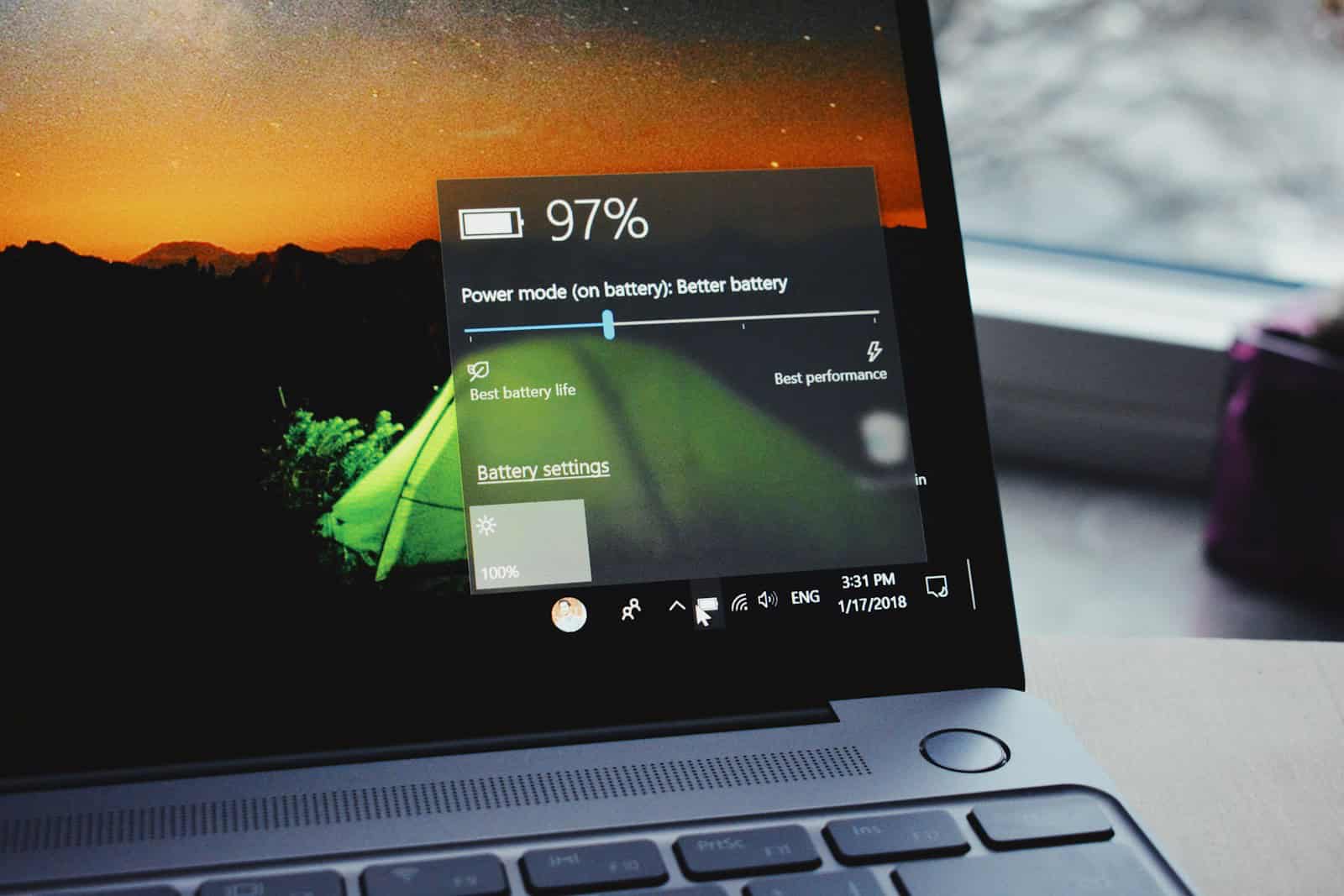
- Power Plan: Make sure you’re using a balanced or power-saving power plan.4 Avoid “High Performance” mode unless necessary.5
- Bluetooth and Wi-Fi: If you’re not using them, turn them off.6
- Peripherals: Unplug any external devices you’re not using, like USB drives or external hard drives.7
2. Resource-Intensive Activities:
- Demanding Applications: Programs like video editing software, games, and streaming services consume a lot of power.8 Close them when not in use.
- Too Many Browser Tabs: Each open tab uses resources.9 Close unnecessary tabs to save power.10
- Background Processes: Some apps run in the background even when you’re not actively using them.11 Check your task manager and close any unnecessary processes.
3. Battery Health:
- Age and Usage: Batteries degrade over time.12 An older battery won’t hold a charge as long as a new one.13
- Overcharging: Constantly keeping your laptop plugged in at 100% can shorten battery lifespan.
- Heat: Excessive heat can damage batteries.14 Make sure your laptop’s vents are clear and that it’s not overheating.
4. Software Issues:
- Operating System Updates: Sometimes, OS updates can introduce bugs that affect battery life. Make sure your OS is up to date, but be aware of potential issues after an update.
- App Malfunctions: A malfunctioning app can consume excessive power.15 Check for updates or consider reinstalling problematic apps.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check Battery Usage: Your operating system likely has a tool that shows you which apps are using the most battery power. Use this to identify and address power hogs.
- Update Drivers: Outdated drivers can sometimes cause power inefficiency.16 Make sure your drivers are up to date.
- Run a Battery Health Check: Some laptops have built-in tools or allow you to download software to check your battery’s health.17 This can tell you if your battery needs replacement.
If the problem persists:
- Calibrate Your Battery: This can help your laptop accurately estimate remaining battery life. Look up instructions for your specific laptop model.
- Contact Support: If you suspect a hardware issue or can’t find the cause of the drain, contact your laptop manufacturer’s support.
By following these tips and troubleshooting steps, you can hopefully improve your computer’s battery life and avoid unexpected shutdowns.
Key Takeaways
- Resource-intensive apps and outdated hardware are major battery drains
- Battery age significantly affects power consumption rates
- Adjusting settings and usage habits can improve battery life
Understanding Battery Drain in Laptops
Laptop battery drain involves complex interactions between hardware, software, and user behavior. Several factors influence battery life, including device age, usage patterns, and system settings.
Factors Affecting Battery Life
Screen brightness significantly impacts battery consumption. Higher brightness levels require more power. Processor-intensive tasks like video editing or gaming drain batteries faster. Wi-Fi and Bluetooth connections also use energy when active.
Running multiple applications simultaneously increases power usage. Background processes and apps continue to drain the battery even when not in use. Outdated or resource-heavy software can lead to inefficient power consumption.
External devices connected to USB ports draw power from the laptop battery. Hard drives consume more energy than solid-state drives (SSDs) due to their mechanical components.
Battery Health and Performance
Lithium-ion batteries degrade over time, reducing their capacity to hold a charge. This natural aging process accelerates with frequent charging cycles and exposure to high temperatures.
Battery calibration helps maintain accuracy in power level reporting. It involves fully discharging and recharging the battery periodically.
Extreme temperatures affect battery performance. Cold weather temporarily reduces battery capacity, while heat can cause permanent damage.
Overcharging or leaving a laptop plugged in constantly may impact long-term battery health. Modern laptops often have built-in protections to prevent overcharging.
Operating System Power Management
Windows and macOS offer power management features to optimize battery life. Power plans allow users to balance performance and energy efficiency.
Battery Saver mode reduces background activity and lowers screen brightness to extend battery life. It activates automatically at low battery levels or can be enabled manually.
Sleep and hibernate modes conserve power when the laptop is not in use. Sleep maintains system state in RAM, while hibernate saves it to the hard drive.
The “powercfg” command in Windows provides detailed battery usage reports and helps identify power-hungry applications.
Regularly updating the operating system and drivers can improve power efficiency through optimizations and bug fixes.