Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, or DHCP, is a network management protocol that simplifies the complexity of configuring devices on IP networks. By automating the assignment of IP addresses, subnet masks, gateway, and other networking parameters, DHCP enables devices to communicate effectively on the internet or local networks. It eliminates the need for administrators to manually assign IP addresses to each device, a process that can be time-consuming and prone to errors.
The operation of DHCP can be thought of as a service provided by a DHCP server, which dynamically distributes network configuration parameters. When a device connects to the network, it sends out a broadcast request for configuration information. The DHCP server responds to this request by leasing an IP address to the device for a specified period of time. This mechanism ensures that IP addresses are efficiently managed and there are no conflicts, which is crucial for the smooth operation of a network.
Image Credit: Gelmo96, CC BY-SA 4.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Key Takeaways
- DHCP is a network management protocol that assigns IP addresses automatically.
- It simplifies device configuration and management on IP networks.
- DHCP servers lease IP addresses and other settings to devices, ensuring efficient network operation.
Understanding DHCP Fundamentals
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, or DHCP, is a network management protocol used to automate the assignment of IP addresses. Knowing how DHCP works helps maintain smooth operations in TCP/IP networks.
How DHCP Works
DHCP assigns each device a unique IP address. The DHCP server keeps a pool of IP addresses and gives them to DHCP clients—devices needing an IP address. When a device connects to the network, it contacts the DHCP server to get an IP.
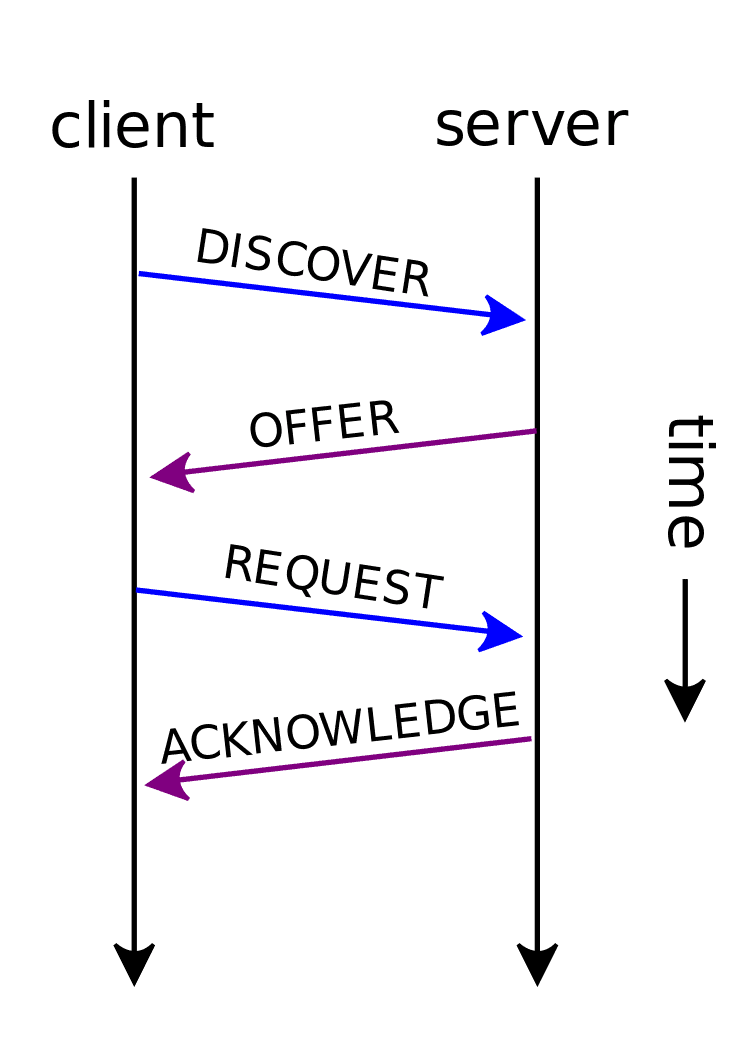
DHCP Lease Process
The lease process begins with the DHCPDiscover message. The client sends it to find a server. The DHCPOffer from the server follows. It includes an available IP address and lease duration. After the client requests the address with the DHCPRequest message, the server sends back an acknowledgment—ACK—confirming the IP address assignment.
IP Address Allocation
DHCP can provide a range of IP addresses, called a scope. Devices receive dynamic IP addresses from this range. The server makes sure each IP address is unique and not permanently tied to a particular device. This approach offers flexibility in managing a network’s IP address pool.
DHCP Configuration Elements
The server settings include options important for devices on the network:
- Subnet Mask: Defines the network’s subnets.
- Default Gateway: Guides data to outside networks.
- DNS Addresses: Helps translate domain names into IP addresses.
The DHCP relay agent is a router feature that passes DHCP messages between clients and servers not on the same subnet. This lets one DHCP server serve multiple subnets.