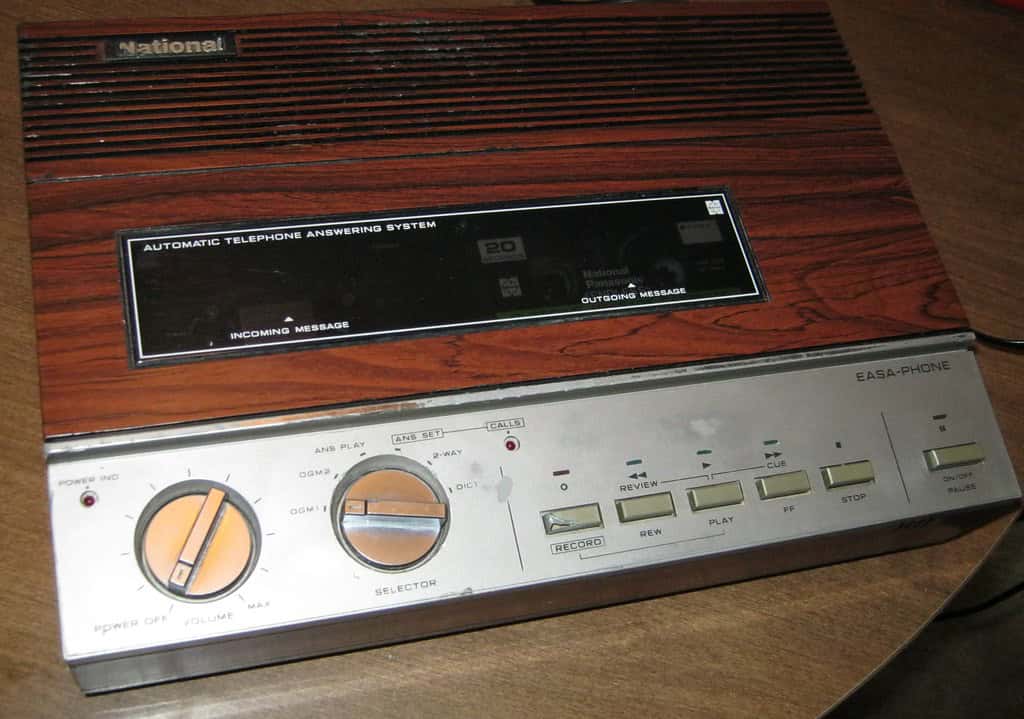
Answering machines were common before voicemail and mobile phones were widely used. These devices recorded messages from callers when no one could answer the phone. Answering machines have been an important part of home communication for years, ensuring that no messages are missed when the phone isn’t answered.
The development of answering machines began with the invention of the telegraphone by Danish engineer Valdemar Poulsen in 1898. This groundbreaking device allowed for magnetic sound recording of telephone conversations. Over time, answering machines have evolved to become more user-friendly, adapting to both analog and digital phone systems.
Typically connected to a landline, an answering machine plays a pre-recorded message to the caller, allowing them to leave a voice message. This functionality makes it easy for people to receive and review calls at their convenience. Whether for a home or office, answering machines continue to play a vital role in managing phone communications effectively.
Image Credit: https://www.flickr.com/photos/7453933@N03/14524663367
The History of Answering Machines
Answering Machines Explained
An answering machine is a device connected to a telephone line. Its purpose? To answer calls when the user is unavailable. It plays a pre-recorded message and records messages from callers. Unlike voicemail, answering machines are physical devices located at the user’s premises. They were a common household item before voicemail and mobile phones became popular.
Types of Answering Machines
There are two main types of answering machines:
- Tape-based answering machines: These older models used cassette tapes to record messages. They were simple to use but had limited storage capacity.
- Digital answering machines: These newer models use digital storage, like flash memory, to record messages. They offer more features, such as caller ID and time/date stamping, and can store more messages.
Features of Answering Machines
Common features of answering machines include:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Outgoing message | The pre-recorded message played to callers. |
| Incoming message | The message left by the caller. |
| Caller ID | Displays the caller’s phone number. |
| Time/date stamp | Records the time and date of each message. |
| Remote access | Allows users to check messages remotely. |
| Message counter | Shows the number of new messages. |
| Call screening | Allows users to listen to messages as they are being recorded. |
| Voice-activated recording | Starts recording when the caller speaks. |
The Decline of Answering Machines
With the rise of voicemail and mobile phones, answering machines have become less common. Voicemail offers similar functionality but is more convenient as it can be accessed from anywhere. Mobile phones allow users to be reached directly, making answering machines less necessary.
Key Takeaways
- An answering machine records calls and messages when the phone owner is unavailable.
- The technology for answering machines began with Poulsen’s telegraphone.
- They play a pre-recorded message and allow callers to leave voice messages.
Overview and Development of Answering Machines
Answering machines have evolved significantly over the years, starting from basic devices using magnetic tape to modern digital systems. Major telecommunication companies played crucial roles in their development, integrating advanced technologies and expanding their use with both wired and cordless phones.
Evolution from Magnetic Tape to Digital
In the early days, answering machines used magnetic tape to record messages. These devices were large and expensive. By the 1960s, machines using magnetic tape became more common with transistors replacing vacuum tubes. This change made them smaller and more reliable.
During the late 1980s, the transition began from tape to digital recording. Digital answering machines offered better sound quality and reliability. Voicemail services provided by telephone companies further advanced how messages were handled. Standalone answering machines started to decline in favor of digital and integrated systems.
Influence of AT&T and Other Telecommunication Giants
AT&T was a key player in the spread of answering machines. In the 1980s and 1990s, AT&T introduced various models integrating advanced features. These innovations included digital recording and smart call blocking.
Other major brands like Panasonic and Sony also contributed to advancements with features such as expandable systems and cordless phone integration. DECT 6.0 technology improved wireless communication for cordless phones. This made answering machines more accessible and functional for household use.
Integration with Landlines and Expansion to Cordless Systems
Originally, answering machines were used with landlines. They were often standalone devices connected to the phone line. As technology improved, manufacturers started integrating answering machines with landline phones, creating built-in systems.
The introduction of cordless phone systems brought another wave of integration. Bluetooth connect to cell technology allowed users to link their mobile phones with home answering systems. This provided greater flexibility and convenience. These devices became more user-friendly, meeting the needs of modern households.
Advancements in Answering System Technologies
Modern answering machines use microchip-based digital recording. This provides excellent sound quality and reliability. They also include features like smart call blocking that helps filter unwanted calls. Some systems offer advanced capabilities like expandable handsets and integration with other smart devices.
Today’s devices are built with features that were unimaginable in early models. The focus is on offering a seamless communication experience. Advancements continue as companies develop new technologies and integrate with existing telecommunications infrastructure.