CAPTCHA, which stands for Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart, is a security feature that websites use to confirm that a user is a real person and not a bot. This test typically involves answering a challenge that humans can easily solve but machines find difficult. These challenges may include typing letters from a distorted image or clicking a checkbox that says “I am not a robot.” The use of CAPTCHAs helps prevent spam and protects websites from automated attacks by ensuring that only humans can perform certain actions. This improves user experience by keeping platforms free from the overwhelming amount of content that bots could potentially produce. While CAPTCHAs add an extra step for users, they play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of online services.
Understanding CAPTCHAs
What Does CAPTCHA Stand For?
CAPTCHA is an acronym for “Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart.” It’s a type of challenge-response test used to determine if a user is human or a bot.
How Does CAPTCHA Work?
CAPTCHAs present users with tasks that are easy for humans to solve but difficult for computers. These tasks often involve:
- Identifying distorted text or images: Users need to type the letters or numbers they see in a distorted image.
- Solving simple puzzles: Users might be asked to select all images containing a specific object or complete a slider puzzle.
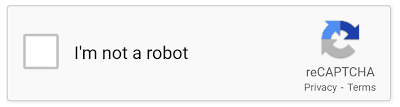
- Checking a box: reCAPTCHA, a popular type of CAPTCHA, often asks users to simply check a box that says “I’m not a robot.”
Why Are CAPTCHAs Used?
CAPTCHAs are used to protect websites and online services from various threats, including:
- Spam: Bots can flood websites with spam comments or messages.
- Account Takeovers: Bots can try to guess passwords and take over user accounts.
- Denial-of-Service Attacks: Bots can overwhelm a website with traffic, making it unavailable to legitimate users.
Types of CAPTCHAs
There are several types of CAPTCHAs, each with its own strengths and weaknesses:
| CAPTCHA Type | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Text-based CAPTCHAs | Users identify distorted letters or numbers. | Simple to implement, effective against basic bots. | Can be difficult for visually impaired users. |
| Image-based CAPTCHAs | Users select images that match a specific criteria. | Harder for bots to solve, more user-friendly. | Can be time-consuming for users. |
| Audio CAPTCHAs | Users listen to a distorted audio recording and type what they hear. | Accessible to visually impaired users. | Less effective against advanced bots. |
| reCAPTCHA | Users check a box or complete a simple task. | Very user-friendly, effective against most bots. | Can be bypassed by sophisticated bots. |
| Behavioral CAPTCHAs | Analyze user behavior to determine if they are human. | Less intrusive for users, harder for bots to bypass. | Requires more sophisticated technology to implement. |
The Future of CAPTCHA
As bots become more sophisticated, CAPTCHA technology is also evolving. Newer types of CAPTCHAs, such as behavioral CAPTCHAs, are becoming more popular due to their improved user experience and effectiveness.
Key Takeaways
- CAPTCHAs distinguish between humans and bots through tests easy for people but challenging for machines.
- They help protect websites against spam and automated attacks.
- Although adding an extra step for users, CAPTCHAs contribute significantly to online security and user experience.
Understanding CAPTCHA
CAPTCHA tests confirm the user is human and prevent bots from misusing web services. These tests are common during website registration and help cut down spam.
Evolution of CAPTCHA
CAPTCHAs have grown from simple text puzzles to complex tests. They began as distorted letters and numbers users had to type. Now, CAPTCHAs use advanced algorithms to challenge bots. Over time, they have adapted to counter more sophisticated spam software. Google reCAPTCHA, for example, uses machine learning and image recognition to detect bot activity.
Types and Implementations
There are several CAPTCHA types:
- Text-based CAPTCHA: Uses distorted text that users must decipher.
- Image CAPTCHA: Displays images of everyday objects for users to identify.
- Audio CAPTCHA: Provides an audio clip of spoken letters or numbers to assist those with visual impairments.
- Checkbox CAPTCHA: This is a simple checkbox that might say “I am not a robot”. It often uses mouse movements to tell if the user is human.
Some websites use social media sign-in, like Facebook, to verify users.
CAPTCHA and User Interaction
CAPTCHAs should be easy for humans but hard for bots. A good CAPTCHA allows quick sign up or sign in for users. If it’s too hard, it can lead to a bad user experience. For users with disabilities, alternatives like audio CAPTCHAs improve accessibility.
Challenges and Solutions
Spam bots and CAPTCHA farms pose big challenges. They can mimic human behavior and pass CAPTCHAs. In response, organizations have developed more complex tests. AI algorithms help CAPTCHAs learn and adapt to new threats. For users, CAPTCHAs must stay simple and not be a barrier to access. It’s a balance between security and usability.