If your M.2 SSD appears in BIOS but is missing in Windows, you’re not alone. This issue is common among users installing a new SSD or upgrading their system. The good news is that in most cases, the problem is easy to fix with a few troubleshooting steps.
Why Is Your M.2 SSD Missing in Windows?
There are several reasons why your M.2 SSD might be recognized in BIOS but not in Windows:
- The Drive Isn’t Initialized – A brand-new SSD needs to be initialized in Windows before it becomes usable.
- No File System or Partition – Without a formatted partition, Windows won’t recognize the SSD in File Explorer.
- No Drive Letter Assigned – Even if the SSD is detected, it won’t appear in File Explorer unless assigned a drive letter.
- BIOS Settings Need Adjustment – Certain BIOS settings, such as SATA mode or NVMe configuration, may need tweaking.
- Outdated or Missing Drivers – Windows might not have the necessary drivers for NVMe SSDs, requiring a manual update.
- Conflicts with Other Storage Devices – Sometimes, other storage devices, such as older SATA drives, can interfere with NVMe detection.
- Hardware or Slot Compatibility Issues – Some motherboards have multiple M.2 slots, but not all support NVMe drives.
How to Fix an M.2 SSD Not Showing in Windows
Here’s how to diagnose and fix the problem:
Step 1: Check Disk Management
- Press Win + X and select Disk Management.
- Look for your M.2 SSD in the list. If it appears as “Unallocated,” you need to initialize and format it:
- Right-click the unallocated space and choose Initialize Disk.
- Select GPT (GUID Partition Table) for modern systems or MBR (Master Boot Record) for older ones.
- After initialization, right-click again to create a New Simple Volume.
- Format the drive as NTFS or exFAT and assign a drive letter.
Step 2: Assign a Drive Letter
If the SSD appears in Disk Management but doesn’t have a drive letter:
- Right-click the SSD’s volume.
- Select Change Drive Letter and Paths.
- Click Add, choose a letter, and confirm.
Step 3: Update Drivers
- Open Device Manager (press Win + X, then select it).
- Expand Disk Drives and look for the SSD.
- Right-click the SSD and choose Update Driver.
- Select Search automatically for drivers and install any available updates.
For NVMe drives, you may need to install the latest drivers from the SSD manufacturer (Samsung, Western Digital, Crucial, etc.).
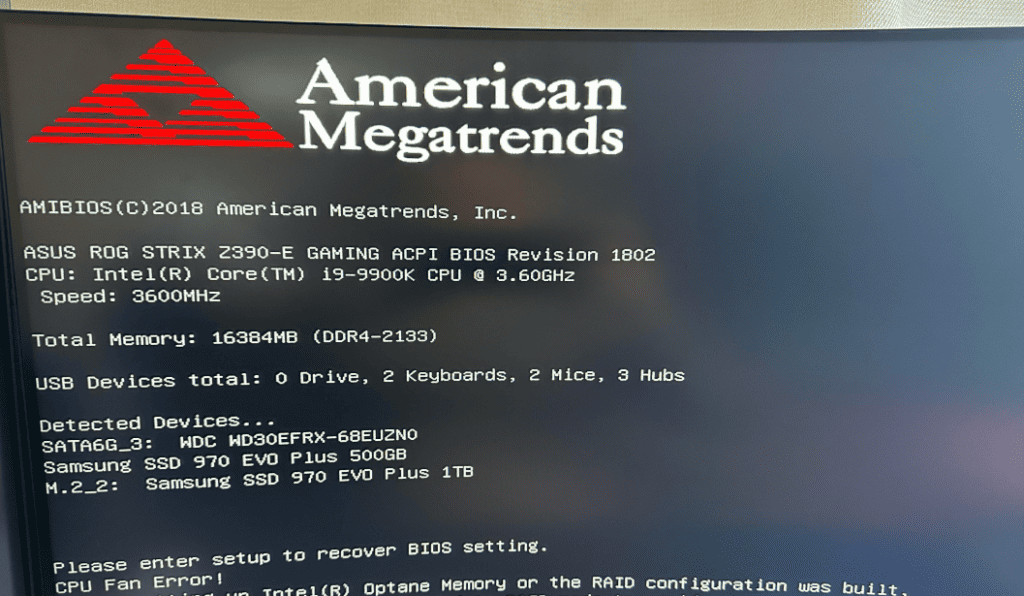
Step 4: Verify BIOS Settings
If the SSD still doesn’t appear:
- Restart your PC and enter BIOS (Press Del, F2, or F12 depending on your motherboard).
- Ensure the SSD is detected in the Boot or Storage Configuration menu.
- Check if NVMe Support or PCIe Storage Remapping is enabled.
- Make sure SATA Mode is set to AHCI (not RAID or IDE).
- Save changes and restart.
Step 5: Install the Latest Chipset and Storage Drivers
Your motherboard manufacturer provides chipset and storage drivers for optimal SSD performance:
- Visit the motherboard manufacturer’s website.
- Download and install the latest chipset drivers and NVMe storage drivers.
- Restart your PC and check again.
Step 6: Test the M.2 Slot
If nothing works:
- Try installing the SSD in another M.2 slot (if available).
- If possible, test the SSD in another computer to confirm it works.
- If the SSD isn’t detected anywhere, it may be faulty.
Final Thoughts
An M.2 SSD not showing in Windows is usually a fixable problem. Most of the time, initializing the disk in Disk Management or updating drivers resolves the issue. However, if BIOS settings or hardware compatibility are at fault, adjusting configurations or testing in another PC may be necessary. By following these steps, your SSD should be up and running in no time.
Key Takeaways
- M.2 SSDs need initialization through Windows Disk Management before they appear in the operating system.
- Check BIOS settings and drive compatibility before troubleshooting in Windows.
- Updating drivers, assigning a drive letter, and formatting with the correct file system can resolve visibility issues.
Troubleshooting BIOS and System Configuration
When your M.2 SSD appears in BIOS but not in Windows, the issue often lies in system configuration settings or driver problems. Addressing these issues requires checking both hardware connections and software settings.
Ensuring Proper M.2 Slot Usage and BIOS Settings
Check which M.2 slot you’re using on your motherboard. Many motherboards have multiple slots with different compatibility for PCIe or SATA-based M.2 drives. Consult your motherboard manual to confirm you’re using the correct slot for your drive type.
In BIOS settings, look for storage configuration options. Some key settings to check:
- SATA Mode: Make sure it’s set to AHCI mode rather than IDE or RAID
- PCIe slots: Some motherboards disable certain SATA ports when M.2 slots are in use
- VMD Controller: On newer systems, disable this if you’re having detection issues
- Secure Boot: Try disabling this temporarily to test if it affects drive visibility
For PCIe NVMe drives that still aren’t detected, check if your BIOS has specific NVMe support. Older systems might need a BIOS update to properly recognize newer NVMe drives.
Updating BIOS and NVMe Drivers
Outdated BIOS firmware can cause M.2 compatibility issues. Visit your motherboard manufacturer’s website to download the latest BIOS version. Follow their specific update instructions carefully, as improper BIOS updates can damage your system.
NVMe driver updates are equally important. Windows usually installs generic NVMe drivers, but manufacturer-specific drivers often work better. For example:
- Download storage controller drivers from your motherboard manufacturer
- For Samsung drives, install Samsung Magician software
- For other brands, check the drive manufacturer’s website
Windows 11 has better native NVMe support than earlier versions. If using Windows 10, ensure you have the latest updates installed.
After updating drivers, check Disk Management (diskmgmt.msc) again. Your M.2 drive might appear but need initialization with GPT or NTFS formatting before becoming visible in File Explorer.
Setting Up the Drive in Windows
When your M.2 SSD appears in BIOS but not in Windows, you’ll need to properly set up the drive in your operating system. This typically involves initializing the drive and creating a partition before Windows can recognize and use it.
Initializing and Partitioning via Disk Management
The most common solution is using Windows Disk Management tool. To access it, right-click on the Start button and select “Disk Management” or type “Disk Management” in the Windows search bar.
Look for a disk labeled as “unknown” or showing “unallocated space.” If you see your drive, right-click on it and select “Initialize Disk.” Choose between MBR or GPT partition styles (GPT is recommended for drives larger than 2TB and for newer systems).
After initialization, right-click the unallocated space and select “New Simple Volume.” Follow the wizard to:
- Specify volume size
- Assign a drive letter
- Format the partition (NTFS is usually best)
- Add a volume label for easy identification
Once completed, your M.2 SSD should appear in File Explorer and be ready to use.
Troubleshooting with Device Manager and Third-Party Tools
If Disk Management doesn’t show your drive, check Device Manager. Search for “Device Manager” in Windows search, then expand “Disk drives” to see if your SSD appears there. If it shows with a warning icon, you may need to update its driver.
For Samsung SSDs, Samsung Magician software can be helpful. This tool can diagnose issues, update firmware, and optimize performance. Other brands often offer similar utilities.
Sometimes the problem lies with Windows Storage Spaces. Check Control Panel > Storage Spaces to ensure your drive isn’t caught in a storage pool.
If nothing works, try these options:
- Run Command Prompt as administrator and use Diskpart commands
- Check for BIOS updates that might improve M.2 compatibility
- Consider asking for help in Microsoft 365 community forums
Frequently Asked Questions
M.2 SSD issues can be frustrating when the drive appears in BIOS but not in Windows. Many users face common problems related to initialization, driver configuration, and BIOS settings.
Why is my M.2 SSD not appearing in Windows Disk Management despite being detected in the BIOS?
The most common reason is that the drive hasn’t been initialized in Windows. New drives need to be prepared before use.
To fix this issue, open Disk Management by typing “diskmgmt.msc” in the Windows search bar. Look for a disk that shows as “unallocated.” Right-click it and select “Initialize Disk,” then format it.
Sometimes outdated storage controller drivers can also cause this problem. Check Device Manager to ensure your drivers are up to date.
How can I enable my M.2 SSD as a boot option in the BIOS settings of an MSI motherboard?
First, enter your MSI motherboard’s BIOS by pressing the Delete key during startup. Navigate to the “Boot” tab or section.
Make sure your M.2 SSD appears in the list of available devices. If it does, you can change the boot priority to set it as the primary boot device.
Some MSI motherboards require you to enable the M.2 slot in a separate section of the BIOS. Look for settings related to PCIe or storage configuration.
What steps should I take if my M.2 SSD is not showing up as a drive within Windows 10?
Check Disk Management first. Open it by right-clicking the Start button and selecting “Disk Management” or by typing “diskmgmt.msc” in Run.
If the drive appears but isn’t assigned a letter, right-click on it and select “Change Drive Letter and Paths” to assign one.
Check Windows Storage Spaces in Control Panel. If your drive appears there, remove it from the pool and delete the pool.
Try disabling AHCI mode in your BIOS if other methods fail. Some drives work better with different storage controller settings.
How do I resolve an M.2 SSD being visible in BIOS but not booting as the primary drive?
Confirm that the operating system is properly installed on the M.2 SSD. Without an OS, the drive can’t boot.
Check your BIOS boot priority settings and make sure the M.2 SSD is set as the first boot device.
Some motherboards have specific M.2 slots that support booting. Check your motherboard manual to ensure you’re using the correct slot.
If the drive was previously working, try resetting the BIOS to default settings. Sometimes incorrect configurations can prevent proper booting.
Is there a reason why a second M.2 SSD would not be recognized by Windows 11 even though it is listed in the BIOS?
Adding a second M.2 SSD can disable certain SATA ports or PCI-E lanes due to limited resources. Check your motherboard manual for compatibility information.
Some motherboards have specific requirements for using multiple M.2 slots at once. Certain slots might share bandwidth with other components.
Windows 11 might need updated drivers to recognize newer M.2 drives. Visit your motherboard manufacturer’s website for the latest drivers.
What could be preventing a newly installed M.2 SSD from appearing as a storage option in Windows?
The drive might need initialization. Open Disk Management and look for unallocated space. Right-click it and select “Initialize Disk.”
Incorrect installation is a common issue. Power down completely, reseat the M.2 SSD, and ensure it’s properly secured with the mounting screw.
Some motherboards require BIOS updates to support newer M.2 drives. Check if your BIOS is up to date.
The M.2 slot might be disabled in BIOS. Check storage configuration settings in your BIOS to ensure the slot is enabled.