AMD’s upcoming Zen 6 “Medusa” CPUs are generating excitement in the tech world. These processors are rumored to feature a significant boost in core count, potentially offering a 50% increase over their predecessors. The new Zen 6 architecture is expected to utilize 12-core CCDs (Core Complex Dies), up from the 8-core CCDs used in the current Zen 5 generation.
This architectural shift could lead to substantial performance improvements. Early reports suggest Zen 6 processors may deliver up to 30% higher single-core performance and 50% higher multi-core performance compared to Zen 3 CPUs. Such advancements would position AMD’s new offerings as strong contenders in the high-performance computing market.
While official release dates remain unconfirmed, industry insiders speculate that Zen 6 “Medusa” CPUs might hit the market in late 2026 or early 2027. AMD continues to push the boundaries of processor technology, aiming to meet the growing demands of gamers, content creators, and professionals who require top-tier computing power.
AMD Zen 6: A Deep Dive into “Medusa”
AMD’s Zen 6 architecture, codenamed “Medusa,” is on the horizon, promising exciting advancements in CPU technology. Let’s break down what we know so far about this upcoming generation of processors.
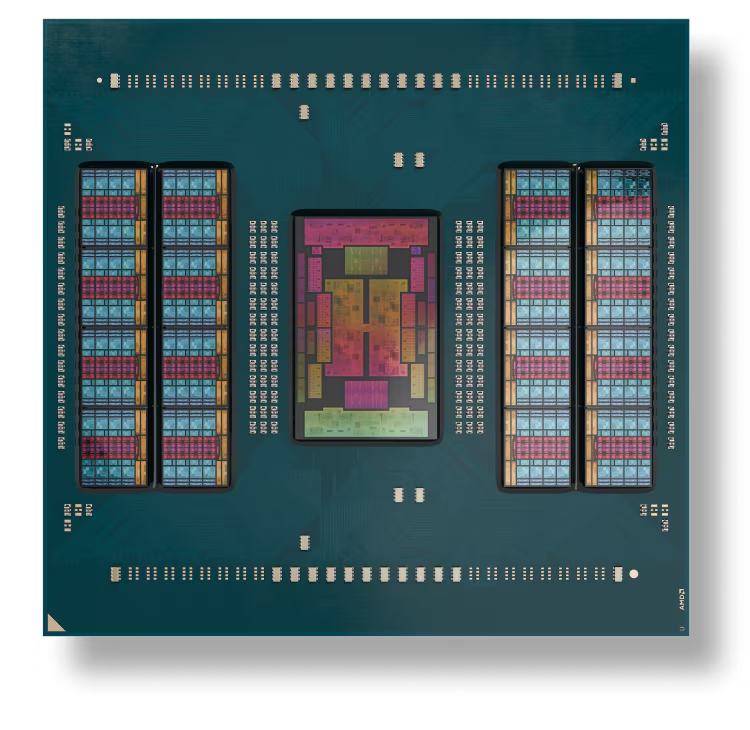
Core Count and Performance
One of the most anticipated features of Zen 6 is a potential significant increase in core count. Rumors suggest a possible 50% jump in cores per CCD (Core Complex Die). This could mean desktop Ryzen processors with up to 24 cores, offering a substantial boost in multi-threaded performance for demanding tasks like video editing, 3D rendering, and gaming. Imagine a Ryzen 9 processor handling complex workloads with unprecedented speed.
Interconnect and Memory
AMD is reportedly exploring a silicon interposer for the interconnect between CPU CCDs and IO dies. This new approach should improve bandwidth and reduce latency. Think of it as a superhighway for data within the processor, allowing information to travel faster and more efficiently. This is especially beneficial for multi-CCD configurations and memory-intensive applications.
Manufacturing Process and Efficiency
Zen 6 CCDs are expected to use TSMC’s advanced 3nm process. This cutting-edge technology packs more transistors into the same space, resulting in better performance and power efficiency. This means cooler, faster processors that consume less energy.
Socket Compatibility and Upgrade Path
Good news for those looking to upgrade: leaks indicate that Zen 6 will likely retain the AM5 socket. This means you can potentially drop a new Zen 6 CPU into your existing AM5 motherboard without needing to buy a new one. This offers a cost-effective upgrade path for current AM5 users.
Release Timeline
While initial whispers suggested a 2027 launch, more recent information points to a possible release window between late 2026 and early 2027. Of course, these dates are still subject to change.
Zen 6 for Servers and Mobile
Zen 6 isn’t just for desktops. It will also power AMD’s next-generation EPYC server processors, codenamed “Venice,” and mobile processors, codenamed “Medusa Point/Medusa Halo.” This means improved performance across AMD’s entire product lineup.
Key Specifications at a Glance
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Architecture | Zen 6 “Medusa” |
| Core Count | Up to 24 cores (rumored) |
| Interconnect | Silicon interposer (expected) |
| Manufacturing Process | TSMC 3nm |
| Socket | AM5 (expected) |
| Release Window | Late 2026 – Early 2027 (potential) |
AMD’s upcoming Zen 6 processors have the potential to shake up the CPU market. The combination of higher core counts, a new interconnect design, and an advanced manufacturing process could deliver a significant leap in performance. These advancements will likely impact everything from gaming and content creation to server performance and mobile computing. The prospect of dropping a cutting-edge Zen 6 CPU into an existing AM5 motherboard makes the upgrade even more appealing.
Key Takeaways
- Zen 6 “Medusa” CPUs are rumored to feature 12-core CCDs, a 50% increase from Zen 5
- Performance gains could reach 30% for single-core and 50% for multi-core tasks
- Launch is expected in late 2026 or early 2027, targeting high-performance computing needs
Architectural Innovations and Performance Enhancements
AMD’s Zen 6 “Medusa” CPUs are set to bring significant improvements in core design, interconnects, and overall performance. These advancements aim to boost gaming and rendering capabilities while maintaining power efficiency.
Zen 6 ‘Medusa’ Core and Cache Design
The Zen 6 architecture is rumored to feature a substantial increase in core count. Reports suggest a potential 50% boost, with 12-core CCDs (Core Complex Dies) replacing the current 8-core design. This change could lead to Ryzen 9 processors with up to 24 cores and 48 threads.
L3 cache sizes are expected to grow proportionally. The increased core count may be accompanied by larger cache pools, potentially reaching 192MB or more when combined with AMD’s 3D V-Cache technology.
Dual-CCD configurations might become more common in mainstream Ryzen processors. This setup could offer improved multi-threaded performance for demanding tasks like content creation and scientific simulations.
Medusa’s Enhanced Interconnects and Efficiency
AMD is likely to introduce advanced interconnect technologies in Zen 6. These improvements may include:
- Higher bandwidth between CCDs
- Optimized silicon interposers for better die-to-die communication
- Refined Infinity Fabric for smoother data flow
These enhancements could reduce latency and improve overall system responsiveness. Power efficiency is expected to improve through better transistor density and refined power gating techniques.
The new architecture might also bring innovations in how cores communicate with memory and I/O, potentially reducing bottlenecks in data-intensive applications.
Gaming and Rendering Performance
Zen 6 “Medusa” CPUs are anticipated to deliver significant gains in gaming and rendering tasks. The increased core count and cache size should benefit:
- High-refresh-rate gaming at 1080p and 1440p resolutions
- CPU-intensive game genres like strategy and simulation
- Ray tracing performance when paired with capable GPUs
For content creators, the additional cores could accelerate:
- Video encoding and transcoding
- 3D rendering in applications like Blender and Maya
- Compile times for large software projects
AMD may also introduce new instruction sets or optimizations tailored for emerging workloads in AI and machine learning, further enhancing Ryzen’s appeal in these growing markets.







