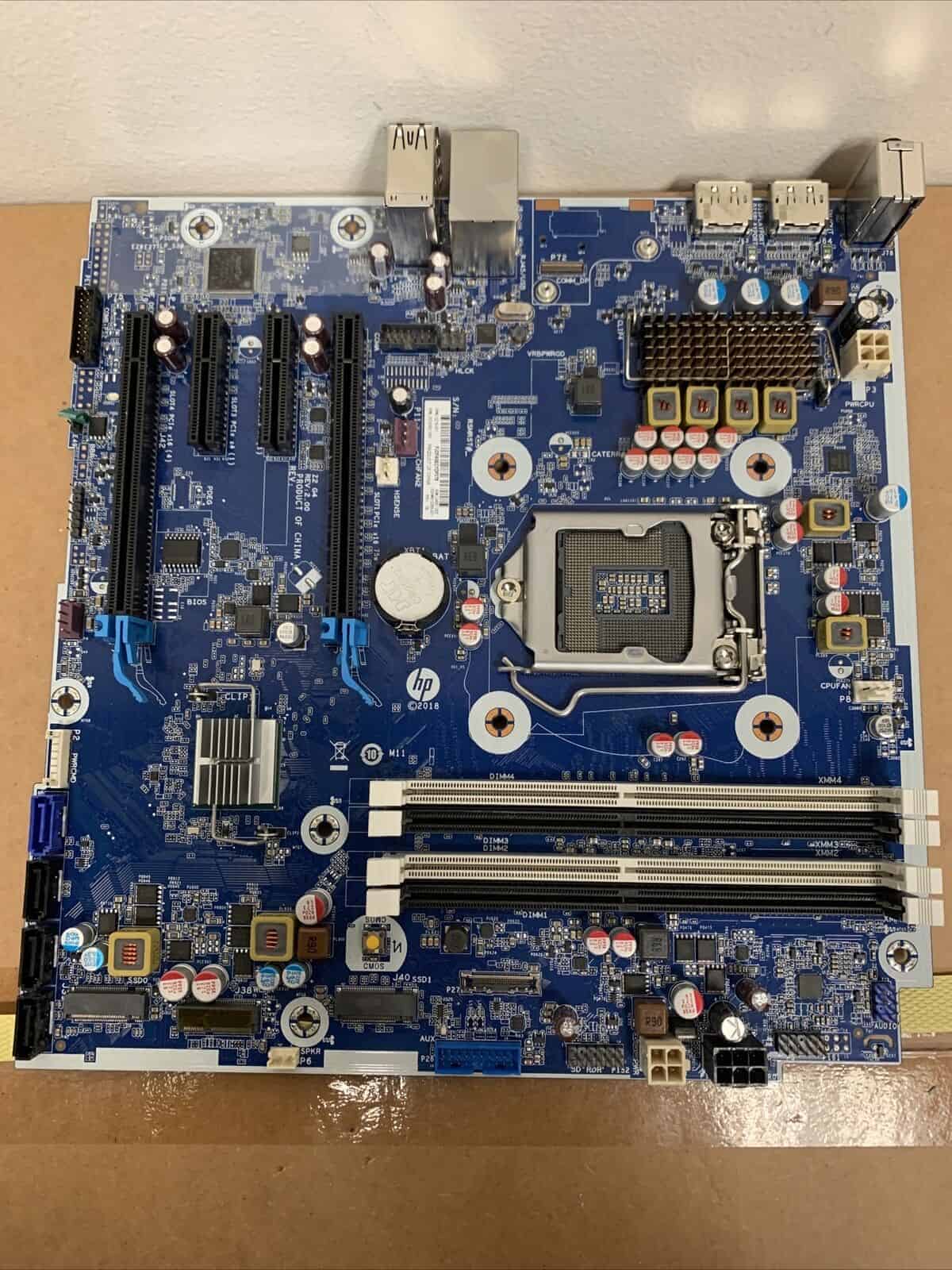
When a computer encounters issues, the motherboard is often suspected as the source of the problem. This critical component serves to connect all the other parts of a computer. It’s imperative to ensure its proper functioning, as any issues with it can render the entire computer inoperable. While it is possible to repair a motherboard, the complexity of the task depends on the severity of the problem.
Simple issues, such as loose wires or dead batteries, are easily fixable, whereas more complex problems may be challenging to diagnose and resolve. When dealing with motherboard repairs, it’s important to consider whether the board has a removable CPU or if the CPU is integrated into the motherboard. If the CPU can be removed, it may be replaceable if it’s malfunctioning. However, in many modern designs, the CPU is soldered to the motherboard. In such cases, if the CPU is faulty, the entire motherboard may need to be replaced.
Tips for Motherboard Repair
Computer motherboards are complex pieces of hardware. They are the backbone of your computer. Motherboards connect everything – the processor (the brain of your computer), RAM (memory), hard drives, video cards, and more. If a motherboard breaks, it can mean buying a whole new computer.
But motherboards don’t always have to be replaced. Sometimes they can be fixed. Whether or not you should attempt a repair depends on the problem. Some problems are easy to fix, but others require expensive tools.
Common Motherboard Problems
Here are some of the most common motherboard problems and their potential solutions:
| Problem | Possible Solutions |
|---|---|
| Computer won’t turn on | Check the power supply and all connections. Replace any faulty components. |
| Blue screen errors | Check for loose connections, bad drivers, or a faulty hard drive. Update outdated drivers. Run system diagnostics. |
| Overheating | Clean dust bunnies from your computer’s case and fans. Consider upgrading your cooling system. |
| Physical damage | Minor scratches and dents may be repairable. More serious damage may require board replacement. |
Should I Repair My Motherboard?
Deciding whether to repair a motherboard depends on the factors below:
- Cost of repair vs. replacement: If the repair is more expensive than a replacement, buying a new motherboard often makes more sense.
- Availability of spare parts: Find out if spare parts, particularly for older motherboards, are easy to find and affordable.
- Technical expertise: Motherboard repair can be complex. If you are not comfortable working with electronics, it may be better to leave it to a professional.

If you decide to go the DIY repair route, make sure to have the right tools and resources. A good guide or tutorial is also essential. Remember, even with careful preparation, there is always a risk of further damaging your motherboard.
Key Takeaways
- A motherboard is essential for computer operation and can often be repaired, depending on the issue.
- Repair complexity varies with motherboard design and the component’s integration level.
- Basic troubleshooting and repairs are often feasible, but severe damage may require replacement.
Understanding Motherboard Repair
When a computer stops working right, the issue could involve the motherboard. This section helps users figure out if their motherboard can be fixed or if it needs replacing.
Identifying Common Motherboard Issues
Problems with the motherboard often lead to the computer not starting, sudden restarts or errors like the blue screen of death. Users might also hear beep codes or see lines on the screen which hint at motherboard failure. It’s key to spot these signs early to handle the issues they point to.
Essential Tools and Safety Measures
To work on a motherboard, one needs tools like a soldering iron and safety gear such as an ESD wrist strap and anti-static mat. This keeps both the person and the computer’s parts safe from static discharge. Collect screws and small containers to keep everything organized.
Steps for Diagnosing Motherboard Problems
To diagnose problems, first turn off the power and detach all cables and peripherals. Then access the motherboard and visually check for damaged capacitors or hardware issues. Next, remove and test components like RAM and the graphics card in another system to rule out these parts as the cause of the problem.
Repair vs. Replacement Considerations
If components like capacitors are damaged, they can be replaced. For issues that need specialized equipment, it might be better to replace the whole board. Consider the motherboard’s age and warranty when deciding if you should fix it or get a new one. A suitable replacement can offer more updated features and stability.
Preventative Maintenance and Care
Keep the computer free from dust and make sure all fans are working to prevent overheating. Check cables for damage or loose connections and ensure the BIOS settings are correct. Regular care keeps the motherboard working smoothly.
Professional vs. DIY Repair
A professional can repair complex motherboard issues quickly. They have the right tools and knowledge. However, simple repairs like replacing components can be done at home. A DIY guide can help if you have some experience. Choose based on the problem’s severity and your comfort with doing repairs.
By following these tips, users can understand the basics of motherboard repair and make informed choices about whether to attempt a repair or opt for a replacement.
Detailed Repair Procedures
When repairing a computer motherboard, it’s crucial to address specific components and issues methodically. This section sheds light on how to handle several common motherboard problems through systematic procedures.
Component-Level Repairs
Repairing a motherboard at the component level often involves diagnosing and replacing faulty capacitors or other damaged components. To replace a capacitor, one must first remove the faulty one using a soldering iron, ensuring not to damage surrounding circuits. The new capacitor, with the same specifications, can then be soldered onto the circuit board.
Troubleshooting Power Issues
If a computer won’t turn on, the problem might be power-related. Check if the power supply unit (PSU) is functional and ensure that all cables connecting to the motherboard are secure. Swap the PSU with a known good one if necessary to test if the motherboard powers up. When handling the PSU, keep in mind safety by disconnecting the power source beforehand.
Addressing CPU and RAM Problems
If a motherboard appears to have CPU or RAM issues, the first step is to inspect the CPU and RAM slots for bent pins or dirt. After cleaning any debris, reseat the CPU and RAM modules carefully, making sure they’re compatible and firmly in place. This might resolve boot-up or performance issues.
Resolving Graphics and Peripheral Connectivity
To fix problems related to graphics cards and peripheral devices, ensure that the expansion cards are seated properly in their slots. Also, confirm that the motherboard is compatible with the graphics card. If the monitor shows no signal, reseat or replace the graphics card to test functionality.
Reassembling and Testing the Motherboard
After all repairs, assemble the motherboard back into the computer case. Connect all panels, cables, and peripherals correctly. Finally, power on the computer to test the motherboard. Keep an eye on the system responses to confirm a successful repair, including the boot process and device connectivity.
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, we address some of the most commonly asked questions about computer motherboard repairs to clarify concerns and provide practical advice.
How much does motherboard repair typically cost?
Motherboard repairs can range from modest to significant costs depending on damage severity and parts required. Prices often fluctuate between $150 and $300, but precise estimates come from professional technicians after a thorough assessment.
What are the common symptoms indicating motherboard damage?
Symptoms of a damaged motherboard include the computer not starting, frequent crashes, and unusual beeping sounds. Other signs involve the blue screen of death (BSOD), issues with recognizing hardware, and system freezing.
What factors commonly cause motherboard failure in laptops?
Overheating, impact from drops, power surges, and liquid spills are common culprits of laptop motherboard failure. Aging and prolonged stress on system components can also lead to malfunction.
Is it feasible to repair a dead motherboard?
While repairing a dead motherboard is sometimes possible, a specialist must first determine the extent of the damage. Minor issues like faulty capacitors can be fixed, whereas severe problems may require a board replacement.
How difficult is it to perform a motherboard repair?
Motherboard repair can be challenging. It demands professional skills, precision soldering, and in-depth knowledge of circuitry. For those without technical expertise or proper tools, it’s best to seek help from a professional.
Can mobile phone motherboards be successfully repaired?
Similar to computers, mobile phone motherboards can often be repaired if the damage isn’t extensive. Trained technicians replace microcomponents and resolve circuit issues, though success rates hinge on the damage level and repair costs.







