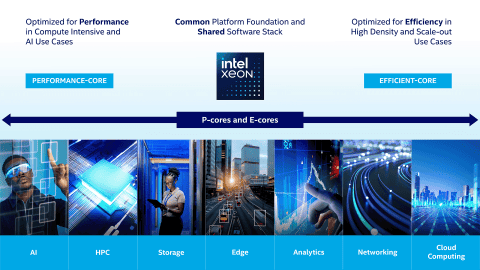
Intel’s latest CPUs bring a new twist to processor design. They mix two types of cores: E-cores and P-cores. E-cores are efficiency cores. They handle background tasks and use less power. P-cores are performance cores. They tackle demanding jobs that need more processing muscle.
E-cores are smaller, simpler cores that sip power while still getting work done. They’re great for things like checking email or running system tasks. This setup helps save battery life in laptops and keeps desktop PCs running cooler. It’s a smart way to balance performance and energy use.
This mix of cores is called hybrid architecture. It’s a big change from the old way of making all cores the same. Now, the CPU can assign tasks to the right type of core. This makes computers more flexible and efficient. It’s an exciting step forward in processor tech.
E-Cores: A Deep Dive into Intel’s Efficiency-Focused Processor Cores
Intel’s hybrid architecture has taken the computing world by storm, introducing a new breed of processor cores known as E-cores. These cores stand for “efficiency-cores,” and they play a crucial role in optimizing performance and power consumption in modern CPUs.
What are E-cores?
E-cores are designed to handle lightweight tasks and background processes with minimal power consumption. They excel at multitasking, web browsing, and running everyday applications, allowing the more powerful P-cores (performance-cores) to focus on demanding tasks like gaming and content creation.
How E-cores Work
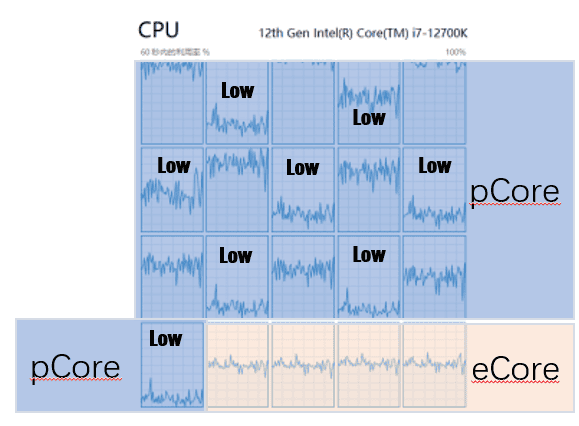
Intel’s hybrid architecture intelligently distributes workloads between E-cores and P-cores. The operating system, with the help of Intel’s Thread Director technology, identifies the nature of each task and assigns it to the appropriate core type. This dynamic allocation ensures that tasks are handled efficiently, maximizing both performance and battery life.
Benefits of E-cores
- Improved Power Efficiency: E-cores sip power compared to P-cores, extending battery life for laptops and reducing energy costs for desktops.
- Enhanced Multitasking: E-cores handle background tasks seamlessly, freeing up P-cores for demanding applications and preventing slowdowns.
- Increased Performance: By offloading less intensive tasks to E-cores, P-cores can operate at higher frequencies, delivering peak performance when needed.
E-cores vs. P-cores
Here’s a table highlighting the key differences between E-cores and P-cores:
| Feature | E-cores | P-cores |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Efficiency and power savings | High performance |
| Clock Speed | Lower | Higher |
| Cache Size | Smaller | Larger |
| Power Consumption | Lower | Higher |
| Ideal Tasks | Web browsing, multitasking, background processes | Gaming, content creation, demanding applications |
E-cores in Action
E-cores are becoming increasingly prevalent in Intel’s latest processors, from mobile CPUs to high-end desktop chips. They are a key component of Intel’s strategy to deliver balanced performance and power efficiency in the modern computing landscape.
As software and operating systems continue to evolve to take full advantage of hybrid architectures, E-cores will play an even more critical role in shaping the future of computing.
Key Takeaways
- E-cores are efficient processor cores that handle less demanding tasks
- Hybrid architecture combines E-cores and P-cores for better performance and power use
- This new design improves battery life in laptops and overall efficiency in desktops
Understanding E-Cores and Hybrid Architecture
Intel’s latest CPUs use a mix of different core types to boost performance and efficiency. This new design combines powerful cores with energy-saving ones to handle various computing tasks.
The Role of E-Cores in Modern CPUs
E-cores, short for efficiency cores, are a key part of Intel’s new CPU designs. These smaller cores use less power and take up less space on the chip. They’re great for background tasks and lighter workloads.
E-cores can handle many tasks at once without using much energy. This helps laptops run longer on battery power. It also keeps desktop PCs cooler and quieter during normal use.
In Intel’s hybrid design, E-cores work with P-cores (performance cores) to get more done. When you’re not doing heavy tasks, the E-cores can handle most of the work. This saves power and extends battery life.
Comparing E-Cores and P-Cores
P-cores are bigger and more powerful than E-cores. They’re built for high-performance tasks like gaming or video editing. E-cores are smaller and use less power, but can still do a lot of work.
Here’s a quick comparison:
- P-cores: Best for single-threaded tasks, high clock speeds
- E-cores: Great for multi-threaded tasks, energy efficient
P-cores can do one job very fast, while E-cores can do many smaller jobs at once. This mix lets the CPU adapt to different workloads. It’s like having a team of specialists and generalists working together.
Intel says their new E-cores are 40% faster than their old Skylake cores at the same power level. This shows how much E-cores have improved.
Evolution of Intel CPU Designs
Intel’s move to hybrid architecture marks a big change in CPU design. For years, CPUs just got more cores that were all the same. Now, they’re using different types of cores together.
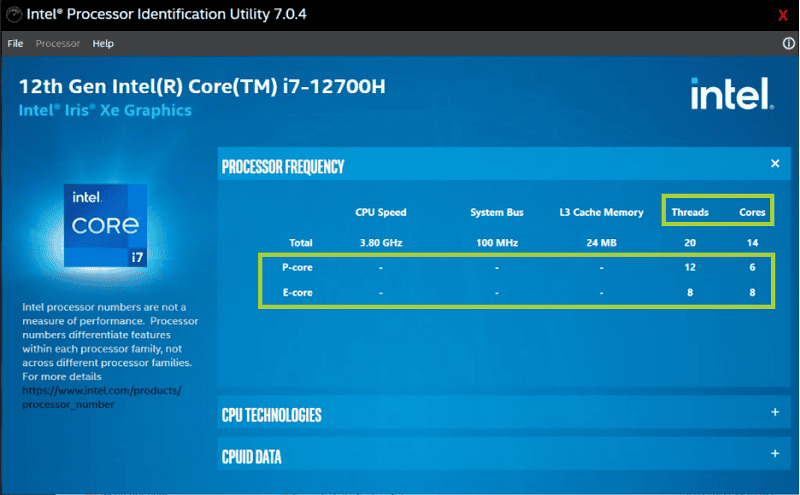
This new approach started with the 12th Gen Intel Core processors. These chips use both Golden Cove (P-cores) and Gracemont (E-cores) designs. The 13th Gen chips built on this, making the cores even better.
The hybrid design lets Intel pack more cores into a CPU. This helps with multi-tasking and complex workloads. It also makes CPUs more flexible, able to balance power and efficiency as needed.
As software gets better at using these different core types, we’ll likely see even more benefits from this design in the future.
Performance Considerations for Efficiency Cores
E-cores bring new capabilities to CPUs, balancing performance and power use. They affect multitasking, energy efficiency, and how tasks are handled across different core types.
Enhancing Multitasking with Multi-Core Processing
E-cores boost a CPU’s ability to handle many tasks at once. They take on background jobs, freeing up P-cores for heavy work. This setup lets the CPU juggle more tasks smoothly.
Windows 11 works well with this core mix. It knows which tasks fit best on E-cores or P-cores. This smart task sorting helps apps run better together.
E-cores can handle multi-threaded tasks too. While not as fast as P-cores, they still add to overall performance. This helps in jobs like video editing or 3D rendering.
The Impact of E-Cores on Energy Efficiency
E-cores shine in saving power. They use less energy than P-cores but still get work done. This matters for laptops and tablets, where battery life is key.
These cores run at lower speeds, often around 3.9 GHz. But they’re great at performance per watt. This means more computing power for less energy used.
In laptops, E-cores can extend battery life. They handle light tasks without waking power-hungry P-cores. This clever design helps devices last longer on a charge.
Intel’s Thread Director Technology
Thread Director is Intel’s smart task manager. It works with the OS to put the right tasks on the right cores. This tech is key to getting the most out of mixed-core CPUs.
It looks at each task’s needs and the current CPU state. Then it decides whether to use E-cores or P-cores. This happens fast, so your computer always feels responsive.
Thread Director shines with Windows 11. Together, they make sure demanding apps get P-cores when needed. Meanwhile, background tasks run on E-cores to save power.
Frequently Asked Questions
E-cores are a newer type of CPU core that brings efficiency and performance benefits. Let’s explore some common questions about this technology.
What are the differences between E-cores and P-cores?
E-cores focus on efficiency, while P-cores prioritize performance. E-cores handle background tasks and less demanding workloads. P-cores tackle more intensive tasks like gaming and video editing. E-cores are smaller and use less power than P-cores.
What purposes are E-cores typically utilized for?
E-cores excel at running background processes and lightweight tasks. They manage system tasks, handle web browsing, and run chat apps. E-cores also take on simple productivity work like email and word processing.
How does having E-cores affect gaming performance?
E-cores can improve gaming by freeing up P-cores for the game itself. They handle background tasks so P-cores focus on rendering graphics and processing game logic. This can lead to smoother gameplay and higher frame rates in some cases.
Can you manually disable E-cores, and what are the pros and cons?
Yes, E-cores can be disabled in BIOS settings on many systems. Pros of disabling include simpler task scheduling and potential gains in some older programs. Cons involve reduced multitasking ability and lower overall system efficiency.
Do AMD processors feature E-core technology similar to their counterparts?
Currently, AMD does not use a hybrid core design like Intel’s E-cores and P-cores. AMD focuses on a single core type across their consumer CPUs. They achieve efficiency through other means, such as chiplet designs and power management features.
What advantages do E-cores offer within a CPU architecture?
E-cores boost multitasking by handling many small tasks at once. They improve power efficiency, extending battery life in laptops. E-cores also allow for higher core counts in CPUs, increasing overall performance potential.







