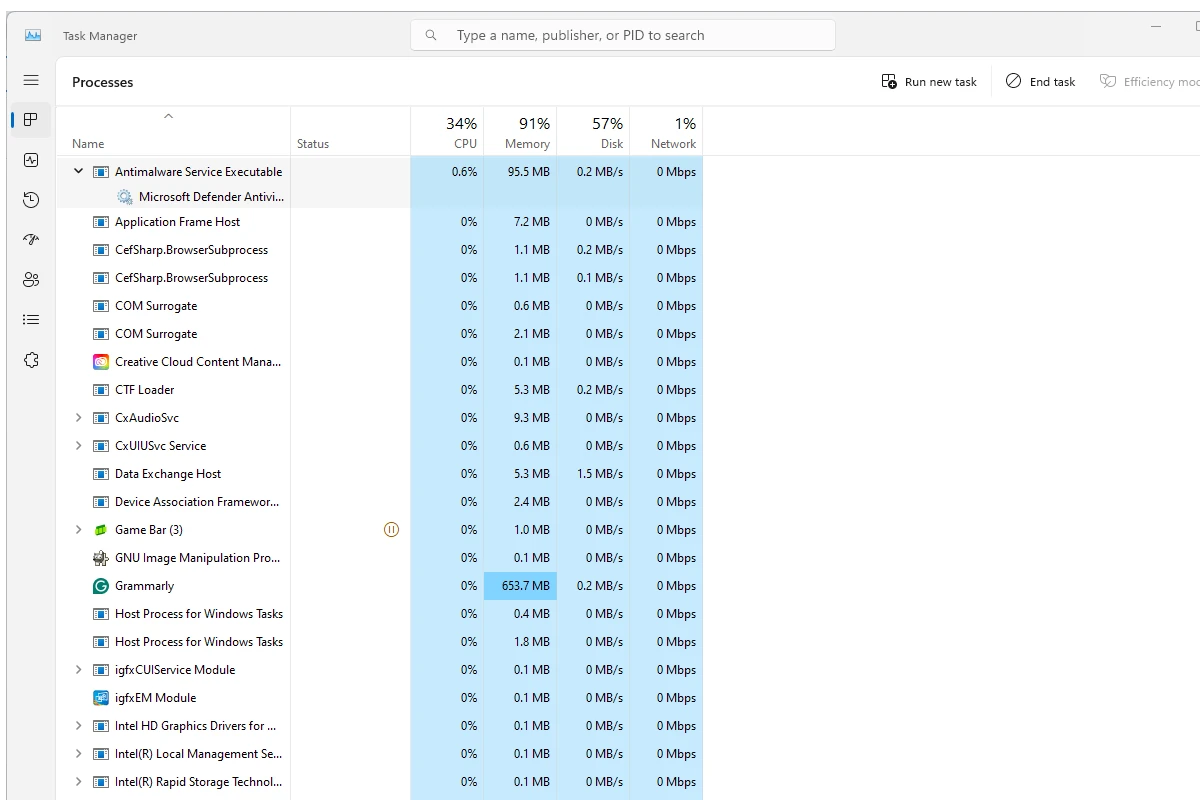
If you are using Windows and cannot see the GPU tab in Task Manager, don’t worry too much. This issue is often caused by a simple setting, outdated drivers, or system configuration errors. The easiest way to fix it if the column is hidden is to simply right click on the top row and select the GPU option. If that option is already selected, then you more than likely have an outdated driver that needs to be updated. To fix that, go to the Device Manager, right-click on the GPU, and select “Update Driver”.
Always make sure to keep your graphics drivers up-to-date, as outdated or corrupt drivers are often the root of most GPU-related issues.
What To Do When Your GPU Goes Missing From Task Manager
Sometimes your computer graphics card (GPU) won’t show in the Windows Task Manager. This problem can make it hard to know how well your programs or games use your GPU. Fortunately, there are several ways to fix this problem.
Make the GPU Column Visible in Task Manager
Sometimes, the issue is simply that the GPU information isn’t being displayed. Here’s how to make sure:
- Open the Windows Task Manager with Ctrl+Shift+Esc.
- Click on the “Processes” tab.
- Right-click on any of the column headings (like “Name” or “CPU”).
- Ensure the “GPU” option has a checkmark next to it.
If this was the problem, you should now see the GPU column. If not, there are other things to try.

Update or Reinstall GPU Drivers
Outdated or corrupt graphics drivers can cause all sorts of problems, including the GPU not showing in Task Manager. Use these steps to update the driver:
- Press the Windows key + X, then choose Device Manager.
- Expand the Display adapters section.
- Right-click on your GPU, then click Update driver.
- Select Search automatically for drivers. Follow the prompts to install available updates.
If that doesn’t work, try reinstalling the drivers with the following steps:
- Repeat steps 1-3 above.
- This time, select Uninstall device and follow the prompts.
- Visit your GPU manufacturer’s website and find the latest drivers for your model.
- Download and install the drivers.
Check for BIOS and Windows Updates
Outdated BIOS firmware or Windows updates could be causing problems. Check with your motherboard manufacturer for relevant BIOS updates. You can manually check for Windows updates like this:
- In the Windows search bar, type “Check for updates”.
- Click the result and follow any prompts to install pending updates.
Hardware Issues
If nothing else works, it’s possible there’s a hardware fault with your GPU or how it connects to your system. Try the following if you feel comfortable working inside your computer:
- Check GPU seating: Make sure the GPU is securely seated in its slot.
- Test a different GPU: If you have another GPU, try replacing your current one to see if it makes a difference.
Troubleshooting Table
| Issue | Possible solutions |
|---|---|
| GPU column not visible | Make the GPU column visible in Task Manager |
| Outdated or corrupt drivers | Update or reinstall your GPU drivers |
| BIOS or Windows updates needed | Check for and install available updates from your motherboard manufacturer and Windows |
| Hardware problem | Try reseating the GPU or testing with a different card |
Troubleshooting Tips and Tricks
Dealing with Hardware Issues
Sometimes, the problem might lie in how your GPU is physically connected to your system. Don’t worry, though; we’ve got you covered with these steps:
Reseating the GPU
- First, turn off your computer completely and unplug it from the power outlet.
- Open the PC case carefully. You might need a screwdriver for this.
- Locate your GPU. It’s usually a big card plugged into a slot on your motherboard.
- Gently push down on the clip or lever holding the GPU in place, then carefully pull the card out.
- Blow away any dust from the slot and the GPU’s contacts with compressed air.
- Line up the GPU with the slot and push it in firmly until you hear a click. Make sure it’s fully seated.
- Close the PC case, plug it back in, and turn it on.
Other Hardware Checks
- Power Supply: Make sure your power supply provides enough wattage for your GPU. Check your GPU’s requirements and compare them to your power supply’s output.
- PCI-e Slot: Inspect the PCI-e slot where your GPU is plugged in. Look for any bent pins or visible damage.
- Professional Help: If you’re not comfortable working inside your computer or if you suspect a hardware fault, consider taking it to a professional repair shop.
Tackling Driver Issues
If updating your drivers didn’t work, here are a few more tricks to try:
- Roll Back Driver: Did the problem start after a recent driver update? You can try rolling back to the previous version. In Device Manager, right-click your GPU, select “Properties”, go to the “Driver” tab, and click “Roll Back Driver”.
- Clean Install with DDU: Display Driver Uninstaller (DDU) is a handy tool for completely removing old drivers. Download it from a trusted source, run it in Safe Mode, and then reinstall the latest drivers from your GPU manufacturer’s website.
- Check for Driver Conflicts: Sometimes, other hardware or software can interfere with your GPU drivers. Try starting your PC in Safe Mode to see if the issue persists. If it doesn’t, you might have a conflict.
The BIOS/UEFI Deep Dive
Your BIOS or UEFI settings play a crucial role in how your computer’s hardware works. Let’s see how they might affect your GPU:
- Accessing BIOS/UEFI: Restart your computer and press a specific key (usually F2, Delete, or Esc) during startup to enter BIOS/UEFI settings. The exact key might vary depending on your motherboard manufacturer, so check your PC’s manual or search online.
- Enabling GPU in BIOS: Look for an option related to your GPU in the BIOS settings. It might be under “Advanced”, “Chipset”, or “Integrated Peripherals”. Make sure your dedicated GPU is enabled if you have one.
- Updating BIOS: Keeping your BIOS updated is a good practice. Check your motherboard manufacturer’s website for the latest BIOS version and instructions on how to update it.
Additional Considerations
- Software Conflicts: Sometimes, software conflicts can cause issues with GPU detection. Try booting your PC in Safe Mode to see if the problem goes away. If it does, you might have a conflicting program.
- Operating System Issues: In rare cases, corrupted system files or Windows bugs can be the culprit. Try running the System File Checker (open Command Prompt as administrator and type “sfc /scannow”) or consider a system restore if other solutions fail.
- Laptop Specific Issues: Laptops often have both integrated and dedicated GPUs. Make sure you’re using the correct one and that your BIOS settings are optimized for it. Also, outdated BIOS versions on older laptops can sometimes cause problems.
Troubleshooting Table
| Issue | Possible Solutions |
|---|---|
| GPU column not visible in Task Manager | Make the GPU column visible in Task Manager |
| Outdated or corrupt drivers | Update or reinstall your GPU drivers, roll back driver, clean install with DDU, check for driver conflicts |
| BIOS or Windows updates needed | Check for and install available updates from your motherboard manufacturer and Windows, access BIOS/UEFI, enable GPU in BIOS, update BIOS |
| Hardware problem | Try reseating the GPU or testing with a different card, check power supply, inspect PCI-e slot, seek professional help |
| Software conflicts | Boot in Safe Mode, identify and remove conflicting programs |
| Operating system issues | Run System File Checker, consider system restore |
| Laptop-specific issues | Check GPU settings, update BIOS on older laptops |
Key Takeaways
- GPU visibility issues in Task Manager are often due to outdated drivers.
- Updating drivers and checking BIOS settings are practical solutions.
- System file checks may resolve underlying hardware detection issues.
Diagnosing GPU Visibility Issues
When the GPU tab is not visible in Task Manager, it’s crucial to confirm the card is properly connected, recognized by the OS, and not disabled in the system settings.
Checking GPU Connection and Power Supply
First, ensure the graphics card is seated correctly on the motherboard. Power down the system, unplug it, and then open the case. The card should be firmly in the PCI-E slot with no gaps. Next, check power cables for a secure connection to both the power supply and the GPU, especially if you have a dedicated GPU that requires additional power.
Verifying GPU Detection in Device Manager
On Windows, press Windows + R, type devmgmt.msc, and press Enter. In Device Manager, look for Display adapters. If your GPU appears here, it’s detected by the OS. If it’s not visible or shows a caution icon, the graphics card driver may need an update or reinstallation.
Assessing BIOS and UEFI Settings
Restart the computer and enter the BIOS or UEFI settings, usually by pressing a key like F2, Delete, or Esc during startup. Check to see if the graphics card is enabled in these settings. The exact pathway depends on the motherboard manufacturer and BIOS version, but you typically find this option under Advanced, Chipset, or Integrated Peripherals.
Solutions to Common GPU Detection Issues
When a GPU is not visible in Task Manager, a few common solutions can rectify the issue. This section outlines precise steps for updating drivers and settings to ensure your graphics processing unit (GPU) appears correctly in the performance tab.
Updating Drivers and Operating System
Updating Graphics Driver:
- Press Windows + R.
- Type
devmgmt.mscand press Enter. - Expand Display adapters.
- Right-click your GPU and select Update driver.
- Choose Search automatically for updated driver software.
Updating Windows:
- Select Settings from the Start menu.
- Click Update & Security.
- Choose Windows Update.
- Click Check for updates.
These steps can ensure you have the latest driver for your specific GPU and the most recent version of Windows, whether it’s Windows 10 or Windows 11.
Resolving Software Conflicts and System File Corruption
Fixing Corrupted System Files:
- Open Command Prompt as an administrator.
- Enter
sfc /scannowto run the System File Checker. - If corruption is found, use the Deployment Imaging Service and Management Tool by entering
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth.
Address Software Conflicts:
- Run your PC in Safe Mode to check for software conflicts.
- Use applications like Display Driver Uninstaller (DDU) to remove old drivers fully, which might cause conflicts.
- Reinstall the graphics driver and restart the system.
These processes can repair corrupted system files and help to resolve any software conflicts that may prevent the GPU from showing up.
Modifying System and Registry Settings
Adjusting Performance Counter Settings:
- Run Command Prompt as an administrator.
- Enter the command
lodctr /rto rebuild performance counter settings.
Editing Registry Settings:
- Type
regeditin the Run dialogue (Windows + R). - Navigate cautiously to the relevant registry entries relating to GPU display.
- Modify as needed, but only if you are confident in making changes to the registry.
By diligently updating your registry or rebuilding performance counters, you may be able to resolve issues preventing the GPU from being detected. Remember, altering registry settings should be done with caution and preferably by advanced users or professionals.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section provides solutions for when the GPU is not visible in Task Manager and outlines steps to diagnose and address graphics card detection issues.
Why is my graphics card not listed in the Task Manager?
A graphics card may not appear in Task Manager due to outdated drivers or incorrect installation. Ensuring the device is properly seated in the PCI-e slot and drivers are current can often resolve this.
How can I resolve the issue of the Task Manager not displaying my GPU usage?
If GPU usage isn’t displayed, open Task Manager and access the Processes tab. Right-click on any column header, ensure the GPU option is checked, and the usage stats should become visible.
What are common troubleshooting steps for a GPU not detected by the system?
To troubleshoot an undetected GPU, check all physical connections first. Then, verify the graphics card is enabled in BIOS and reinstall drivers if necessary.
In Windows 11, what steps should be taken if the GPU does not appear in Task Manager?
For Windows 11, open Device Manager, expand Display adapters, and update the driver of your GPU. If the GPU still doesn’t show, reinstalling the driver might be needed.
What could be causing my AMD or NVIDIA GPU to be absent from Device Manager and Task Manager?
AMD or NVIDIA GPUs might not show up if the drivers are corrupted or the BIOS settings have disabled the GPU. Clean installation of drivers or enabling the GPU in BIOS could help.
What methods can be employed to ensure Task Manager recognizes my GPU in the Processes tab?
To make sure the GPU shows up in the Processes tab, add a GPU column by right-clicking on the header row and selecting GPU details. Ensure the drivers are updated and the system recognizes the hardware properly.