Intel’s upcoming Panther Lake CPUs mark a significant milestone in the company’s semiconductor manufacturing journey. These processors will be the first to utilize Intel’s advanced 18A process node, representing a 1.8-nanometer technology. The shift to the 18A node signifies Intel’s commitment to regaining its leadership position in chip manufacturing.
Intel has already distributed initial engineering samples of Panther Lake to customers, with eight successfully powering on the chips. This development demonstrates Intel’s progress in bringing the new technology to market. Panther Lake’s use of the 18A process is expected to deliver substantial improvements in performance and efficiency compared to previous generations.
The introduction of Panther Lake on the 18A node also represents Intel’s strategy to reduce reliance on external foundries. Over 70% of Panther Lake chips will be manufactured in-house, showcasing Intel’s renewed focus on vertical integration and technological independence.
Panther Lake and Intel’s 18A Process
What is Intel 18A?
Intel 18A is Intel’s next-generation process node. It’s set to arrive in 2025. This new node will use two key technologies: RibbonFET and PowerVia. RibbonFET is Intel’s name for gate-all-around transistors. This design lets them pack more transistors onto a chip. PowerVia puts the power delivery network on the back of the chip. This frees up space on the front for more transistors. Intel says 18A will give a 10% performance per watt increase. This means better speed with less power use. This is very important for data centers and AI.
Panther Lake: The First 18A CPU
Panther Lake will be the first Intel CPU to use the 18A process. This is a big deal for Intel. It shows they are moving forward with their plans. Panther Lake will use new “Cougar Cove” P-Cores. These are the main processing units in the CPU. Using 18A means Panther Lake should have better performance and use less power. This is important for both desktop PCs and laptops.
Why 18A Matters
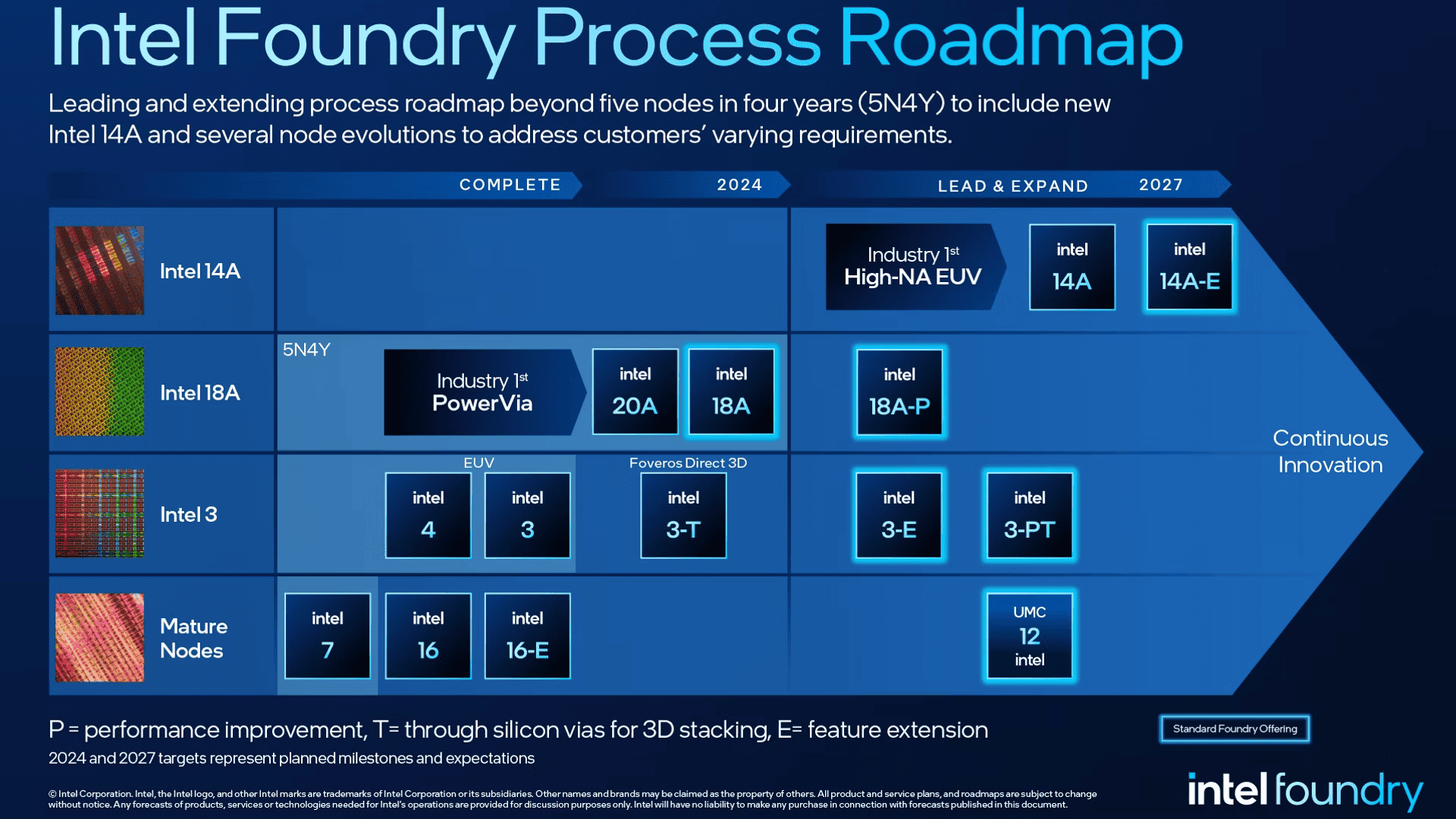
18A is part of Intel’s plan to make five new process nodes in four years. This is called “5N4Y.” Intel wants to lead in chip making again. 18A is a key step in this plan. It also means Intel will make more of its own chips. In the past, they used other companies like TSMC for some parts. With 18A, Intel will make the main part of the CPU themselves.
Comparing Intel’s Nodes
Here is a simple table comparing some of Intel’s recent and upcoming process nodes:
| Process Node | Key Features | Expected Year |
|---|---|---|
| Intel 7 | Improved FinFET transistors | 2021 |
| Intel 4 | First use of EUV lithography | 2022 |
| Intel 3 | Further FinFET improvements | 2023 |
| Intel 20A | RibbonFET and PowerVia | 2024 |
| Intel 18A | Further RibbonFET and PowerVia improvements | 2025 |
What This Means for Users
For people who buy computers, Panther Lake and 18A mean better performance. Games should run faster. Programs will open quicker. Laptops could have longer battery life. For businesses, especially data centers, 18A means more computing power for the same amount of energy. This can save money on electricity.
The Bigger Picture
Intel’s move to 18A is important for the whole tech industry. It shows that chip technology keeps getting better. It also creates more competition between chip makers. This competition helps drive innovation and lower prices.
Looking at Intel’s Foundry Services
Intel Foundry Services (IFS) is Intel’s business that makes chips for other companies. 18A will be available for IFS clients. This means other companies can use Intel’s advanced technology to make their own chips. This could lead to more varied and powerful devices.
How 18A Affects AI
Artificial intelligence (AI) needs a lot of computing power. Intel’s new technology, called 18A, can handle these heavy workloads. With better performance and efficiency, 18A can make AI faster and easier to access. Intel says 18A will help its clients make better processors for AI. This new technology is part of Intel’s plan to regain market share and lead in chip technology. Panther Lake will be the first real example of what 18A can do. This is something to watch in the coming years.
Intel’s focus on 18A is not just about creating faster CPUs; it’s also about building a stronger manufacturing base in the US. This has become more important in recent years due to global supply chain issues. By producing more chips domestically, Intel can secure the supply of advanced technology for the US, which is vital for national security and economic reasons. This emphasis on local production is a key part of Intel’s long-term strategy.
Intel is not only making chips for computers and servers but is also developing chips for devices like cars and industrial equipment. These devices also need powerful and efficient chips, and 18A can meet those needs. This shows that Intel is exploring many different markets for its technology. This diversification can help Intel grow and stay competitive.
Intel’s commitment to advancing its process technology with nodes like 18A shows its dedication to innovation and its intent to remain a major player in the semiconductor industry. This commitment is important for the entire tech world. The semiconductor industry is a crucial part of the global economy. Chips are used in nearly everything, from phones to cars to medical devices. Intel’s progress with 18A signals that this important industry is moving forward. This progress is essential for developing new technologies and improving existing ones.
The development of 18A also has implications for quantum computing. While it may not be directly related in the short term, advancements in transistor density and power efficiency will support future advancements in quantum computing technologies. As quantum computing evolves, it will likely rely on advanced manufacturing processes like those used for 18A. This connection shows the long-term importance of Intel’s work in process technology.
Key Takeaways
- Panther Lake CPUs will be the first to use Intel’s advanced 18A process node
- Initial engineering samples have been powered on by customers
- Intel aims to manufacture over 70% of Panther Lake chips in-house
Panther Lake and Intel’s Process Technology Evolution
The semiconductor industry is working to create smaller, faster, and more efficient chips. Intel, a leading company in this area, is developing a new process called 18A. This technology will be used in future CPUs, starting with the new Panther Lake processors. The transition to 18A includes important improvements in chip design and manufacturing, aiming to enhance performance and power efficiency. This change is not only about making computers faster; it also impacts areas like artificial intelligence, data centers, and national security. Intel’s advancements in this field indicate the future direction of computing technology.
Panther Lake represents a significant milestone in Intel’s semiconductor manufacturing evolution. This next-generation CPU showcases Intel’s advanced 18A process node, marking a leap forward in transistor density and performance.
The Significance of Panther Lake in Intel’s Lineup
Panther Lake CPUs will be the first to utilize Intel’s 18A process technology. This positions Panther Lake as a critical product in Intel’s roadmap. The CPU is expected to offer substantial improvements in performance and efficiency compared to its predecessors.
Intel has powered on Panther Lake samples and booted operating systems. This achievement occurred less than two quarters after tape-out, indicating rapid progress in development. Panther Lake is on track to start production in 2025.
The CPU will feature advanced architectures for both Performance Cores and Efficiency Cores. These may include Lion Cove and Skymont designs, though exact details remain unconfirmed.
Breaking Down the 18A Process Node
Intel’s 18A process node represents a 1.8nm-class technology. It incorporates two key innovations:
- RibbonFET: A gate-all-around transistor design for improved performance and efficiency.
- PowerVia: A backside power delivery method that enhances signal integrity and power efficiency.
The 18A node follows Intel’s process technology roadmap:
- Intel 4 (7nm-class)
- Intel 3 (5nm-class)
- Intel 20A (2nm-class)
- Intel 18A (1.8nm-class)
This rapid progression demonstrates Intel’s commitment to regaining process leadership in the semiconductor industry.
Competition and Market Context
Panther Lake and the 18A process are crucial for Intel to compete with TSMC and Samsung. These rivals have been leading in advanced node production for several years.
Intel aims to leapfrog competitors with 18A, potentially offering superior performance and efficiency. This could help Intel regain market share in both client and server CPU markets.
The success of Panther Lake may also attract more customers to Intel Foundry Services. High-performance 18A chips could appeal to companies seeking cutting-edge manufacturing capabilities.
Intel Foundry Services and Manufacturing Strategy
Intel plans to produce over 70% of Panther Lake chips in-house. This aligns with the company’s IDM 2.0 strategy, emphasizing internal manufacturing capabilities.
Intel Foundry Services will play a key role in commercializing the 18A process. The company is actively seeking external customers for this advanced node.
Panther Lake’s development demonstrates Intel’s renewed focus on execution and innovation. By delivering 18A on schedule, Intel aims to restore confidence in its manufacturing prowess and technological leadership.