Intel’s processor naming system has evolved, with the introduction of the new Core Ultra series marking a significant shift. The Core Ultra family includes Core Ultra 9, Core Ultra 7, and Core Ultra 5 processors, representing different performance tiers. This new naming convention simplifies the identification process for consumers and tech enthusiasts alike.
The Core Ultra processors feature a SKU number of 1 or 2, indicating their generation. For mobile processors, suffixes like H, U, or V provide additional information about their specifications and intended use. These changes reflect Intel’s focus on clarity and performance differentiation in their product lineup.
Decoding Intel Processor Names: A Guide to the Core Series and New Core Ultra
Intel recently revamped its processor naming scheme, introducing the new Core Ultra series alongside the existing Core series. Understanding these names can help you choose the right processor for your needs.
Intel Core Series
Credit: Intel
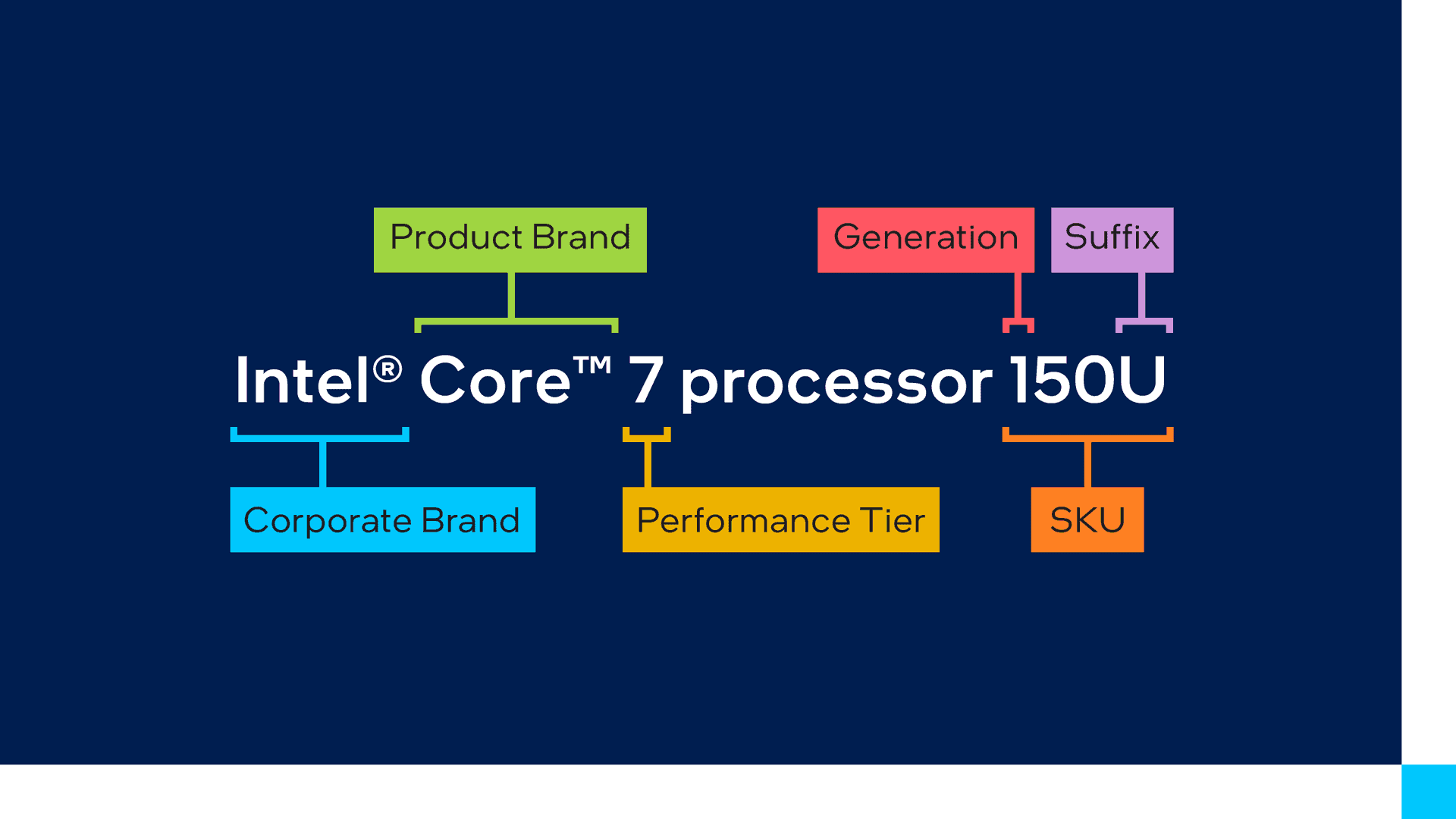
The Intel Core series remains the foundation of Intel’s consumer processor lineup. Here’s how to decipher the names:
- Brand: Intel Core i3, i5, i7, i9 (indicates relative performance level)
- Generation: The first digit(s) of the processor number (e.g., 13th Gen = 13)
- SKU Number: The remaining digits in the processor number (higher numbers generally indicate better performance within a generation)
- Suffix: A letter at the end indicates the processor’s capabilities (see table below)
Example: Intel Core i7-13700K
- Intel Core i7: High-performance processor
- 13: 13th generation
- 700: SKU number
- K: Unlocked for overclocking
Intel Core Ultra Series
Credit: Intel
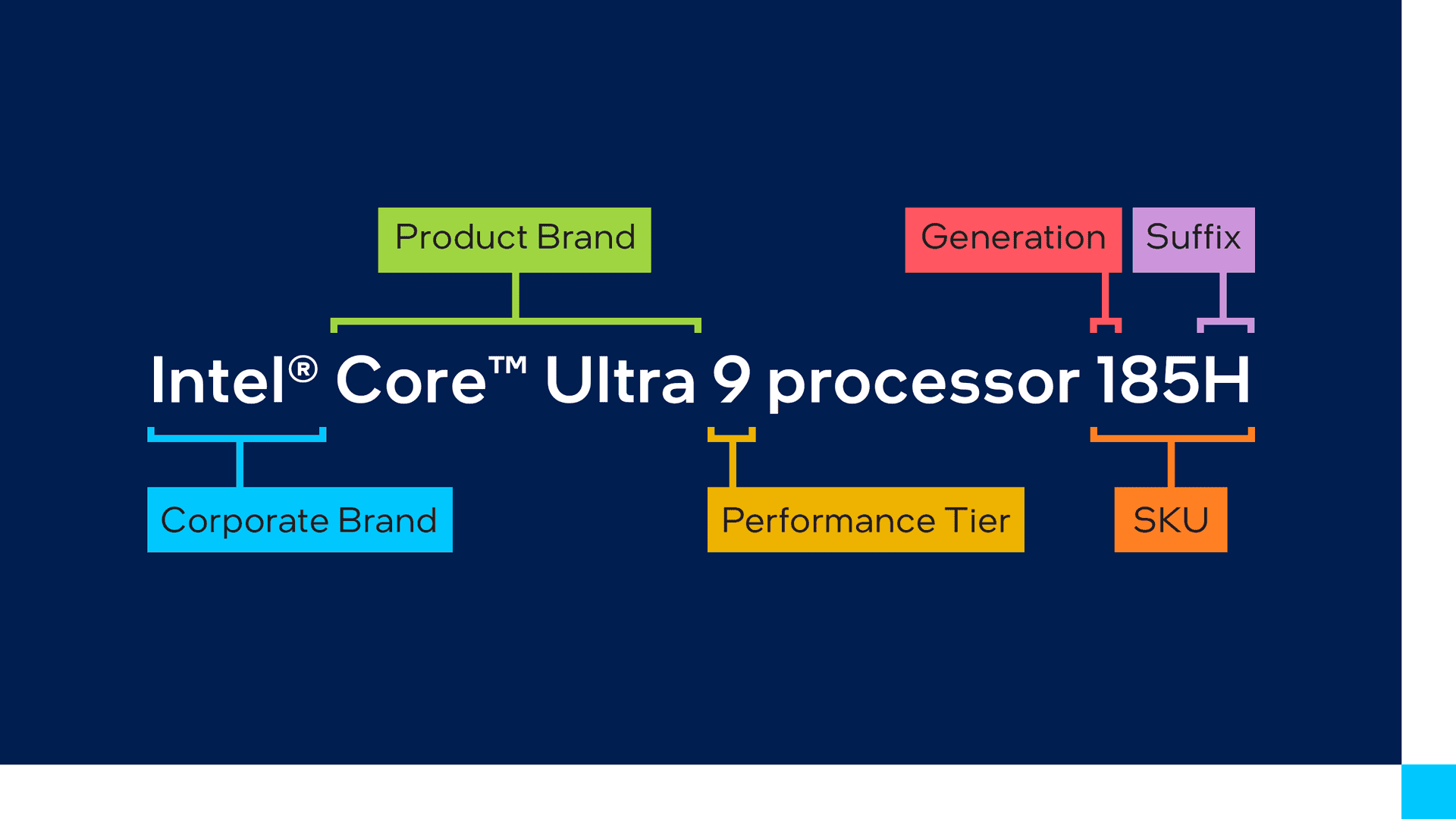
The Core Ultra series represents Intel’s latest processors with enhanced capabilities, particularly in AI and integrated graphics.
- Brand: Intel Core Ultra 5, 7, 9 (indicates relative performance level)
- Generation: Represented by a “1” or “2” in the processor number (e.g., “1” = first generation)
- SKU Number: The remaining digits in the processor number (higher numbers generally indicate better performance within a generation)
- Suffix: A letter at the end indicates the processor’s capabilities (see table below)
Example: Intel Core Ultra 7 165H
- Intel Core Ultra 7: High-performance processor
- 1: First generation
- 65: SKU number
- H: High-performance laptop processor
Suffixes for Intel Core and Core Ultra Processors
| Suffix | Meaning |
|---|---|
| K | Unlocked for overclocking (desktop) |
| F | No integrated graphics (desktop) |
| KF | Unlocked, no integrated graphics (desktop) |
| T | Power-optimized (desktop) |
| S | Special edition (desktop) |
| X/XE | High-end desktop (HEDT) |
| H | High-performance (laptop) |
| HK | High-performance, unlocked (laptop) |
| HX | Highest-performance, unlocked (laptop) |
| P | Performance-optimized (thin and light laptops) |
| U | Power-efficient (laptop) |
| Y | Extremely power-efficient (laptop) |
Important Notes
- The “i” is dropped from the Core Ultra series.
- Not all suffixes are used in both series.
- Intel may introduce new suffixes in the future.
By understanding this naming convention, you can decode Intel processor names and make informed decisions when choosing a CPU for your computer.
Key Takeaways
- Intel’s new Core Ultra series simplifies processor naming conventions
- Core Ultra processors use numbers and suffixes to indicate performance and features
- The new naming system helps consumers easily identify processor capabilities
Understanding Intel Processor Naming Conventions
Intel’s processor naming conventions provide crucial information about performance, features, and target applications. The naming scheme has evolved over time, reflecting advancements in technology and market segments.
Intel Core Series Overview
Intel Core processors form the backbone of the company’s consumer and business offerings. The series includes Core i3, i5, i7, and i9 models, each targeting different performance tiers. Core i3 suits basic computing needs, while Core i9 caters to high-end users and professionals.
The latest addition is the Intel Core Ultra series. These processors, built on the Intel 4 process, feature integrated NPUs and Intel Arc GPUs. They come in Core Ultra 5, 7, and 9 variants, designed for thin and light laptops with enhanced AI capabilities.
Deciphering the Naming Scheme
Intel’s naming scheme follows a specific pattern:
[Brand] [Generation] [SKU] [Suffix]
For example: Intel Core i7-13700K
- Brand: Core i3/i5/i7/i9 or Core Ultra
- Generation: Two-digit number (e.g., 13 for 13th gen)
- SKU: Three-digit product differentiation number
- Suffix: Letters indicating special features
Common suffixes include:
- K: Unlocked for overclocking
- F: No integrated graphics
- H: High-performance mobile
- U: Ultra-low power mobile
Evolution of Intel Processors
Intel’s processor lineup has undergone significant changes since the introduction of the Core series in 2006. The Core 2 Duo and Core 2 Quad processors marked a departure from the previous Pentium architecture.
Subsequent generations brought improvements in performance, power efficiency, and integrated graphics. The introduction of hybrid architecture in recent generations combines performance and efficiency cores for optimal power management.
The latest Intel Core 14th gen and Core Ultra processors showcase advancements in AI capabilities, graphics performance, and power efficiency. These chips aim to meet the growing demands of content creation, gaming, and productivity applications.







