Intel is preparing to make a serious push into the high-performance GPU market with its upcoming Arc B770, part of the next-gen Battlemage (Xe2) architecture. Although not yet officially revealed, leaks, driver entries, and hardware shipping manifests are painting a clear picture: the B770 is real, and it’s aiming directly at the mid-to-high-end gaming segment.
What Is the Arc B770?
The Arc B770 is expected to be the flagship consumer card in Intel’s Battlemage lineup, succeeding the Alchemist-based A770. Built on the Xe2 GPU architecture, the B770 represents Intel’s most ambitious attempt yet to compete with AMD and NVIDIA, particularly in the $400–$600 GPU bracket. It will likely be positioned to go head-to-head with NVIDIA’s RTX 5060 Ti and AMD’s Radeon RX 7600 XT or even RX 8700-class cards, depending on final specs.

Expected Specs (Unofficial, But Widely Reported)
| Spec | Details |
|---|---|
| Architecture | Xe2 Battlemage |
| GPU Die | BMG-G31 |
| Xe Cores | 32 (equivalent to 4,096 shaders) |
| VRAM | 16GB GDDR6 |
| Memory Bus | 256-bit |
| Ray Tracing | 2nd Gen Hardware RT Units |
| Display Outputs | Likely DP 2.1 + HDMI 2.1 |
| TDP | Estimated ~225–275W |
This configuration is a major step up from the Arc A770’s 16GB on a 256-bit bus, and signals that Intel is aiming for performance on par with NVIDIA’s AD104 chips or AMD’s Navi 32-based GPUs.
Latest Development Clues
Intel has yet to formally announce the B770, but several indicators strongly suggest the GPU is nearing completion:
- Mesa Driver Leaks: Linux Mesa graphics drivers recently added four new Battlemage IDs, hinting at various GPU variants, including one strongly believed to be the B770.
- Shipping Manifests: Intel has reportedly shipped BMG-G31 GPU dies to its assembly partners, suggesting the chip is past the design stage and in physical production.
- Power Supply Guidance: Early engineering guidance suggests the B770 may require a PSU rated at 650W or higher, with a 12V-2×6 (formerly 12VHPWR) connector, similar to the RTX 4080.
What Intel Is Saying
Intel has been coy about the B770’s existence, but social media responses like “Stay tuned” and the absence of denials when asked directly about Battlemage’s higher-end models suggest that the company is deliberately building anticipation. This also tracks with Intel’s broader GPU strategy to incrementally scale up from budget models to premium offerings.
Intel’s Tom Petersen, in past interviews, acknowledged that future GPUs would offer improved power efficiency, better software support, and more consistent performance across games—three areas where Arc Alchemist struggled at launch.
Software & Driver Readiness
Intel’s biggest challenge with the Arc A-series wasn’t the hardware—it was the software. Frame pacing, DX11 performance, and inconsistent optimization plagued early Arc drivers. However, driver improvements over the past year have closed much of that gap. Intel has been integrating AI-based upscaling and improving frame generation support, which should be fully mature by the time B770 arrives.
If Battlemage launches with a polished software stack, the B770 could offer competitive real-world performance—not just on paper.
Release Date Window
While no official launch date is confirmed, most industry insiders expect the Arc B770 to debut in Q4 2025, possibly alongside other high-end Battlemage GPUs. This timeline fits with Intel’s rollout of lower-tier B570 and B580 models earlier in the year and positions the B770 for a holiday season release—an ideal time to capture gaming market share.
Will It Be Worth It?
Intel’s Arc B770 could disrupt a GPU market still dominated by two players. If priced aggressively (as Intel has done before) and paired with strong drivers and power-efficient architecture, it may undercut rival offerings while delivering solid 1440p and even 4K gaming performance.
Intel has a lot to prove—but if the B770 lives up to the specs and expectations, it might be one of the most important GPUs of the year.
Stay tuned as we track Intel’s announcements over the coming months. We’ll update with benchmarks, pricing, and real-world testing as soon as the B770 hits the scene.
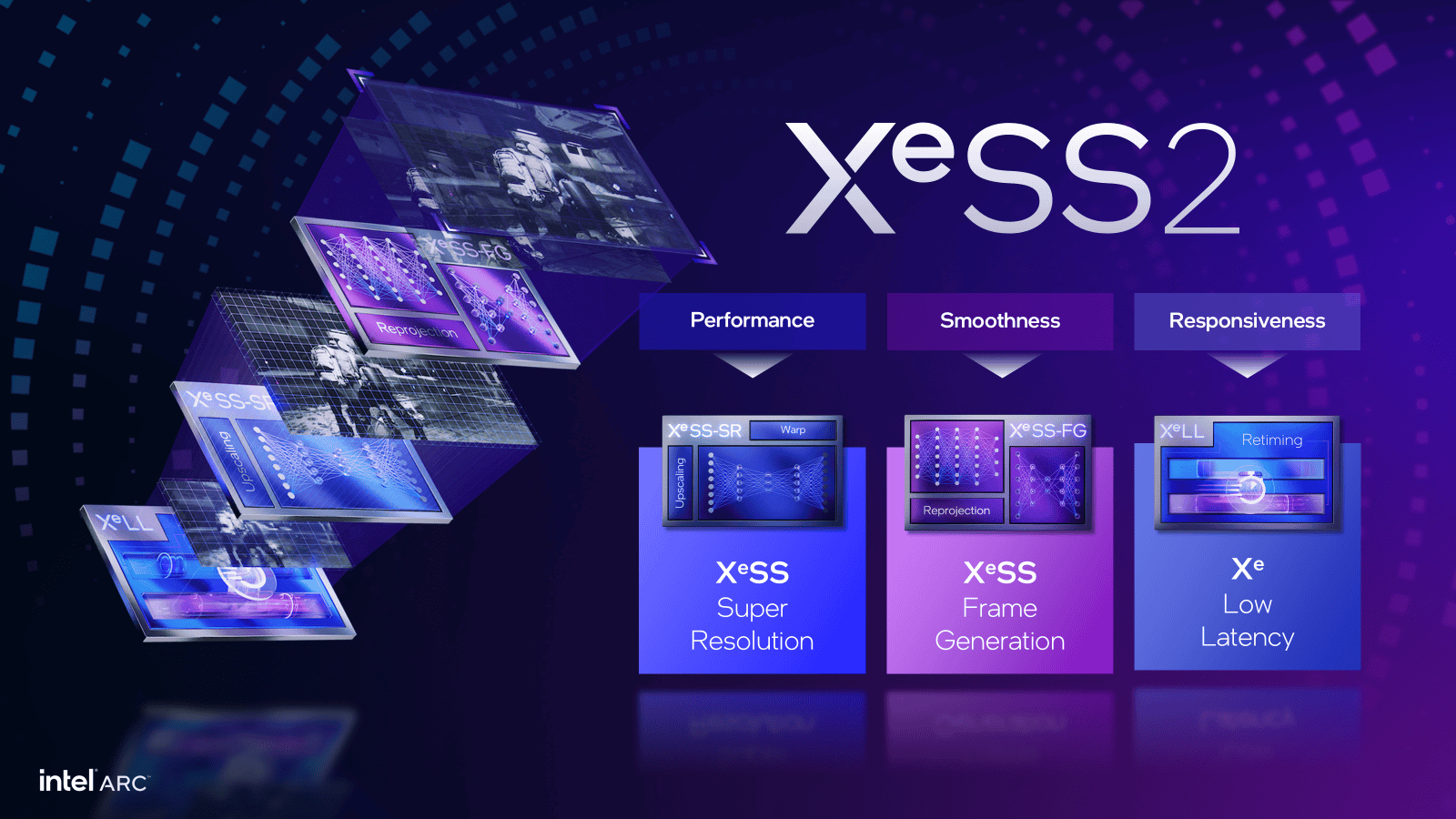
Intel XeSS 2 SDK Goes Open Source
Intel’s new XeSS 2 SDK has finally reached developers, bringing advanced upscaling features to help boost game performance. Despite rumors, the technology remains closed-source with precompiled libraries rather than accessible code. The XeSS 2.0.1 SDK introduces several new capabilities including XeSS-SR, XeSS-FG, and XeLL while supporting both DirectX 11 and newer game engines.
The SDK arrives as a welcome addition for game developers working with Unity and Unreal Engine 4/5. Intel’s AI-based upscaling technology aims to drastically increase frame rates while maintaining high visual quality. This puts it in direct competition with NVIDIA’s DLSS and AMD’s FSR technologies in the growing field of image upscaling solutions.
While many hoped Intel would take an open-source approach with XeSS 2, the company has kept the core algorithms proprietary. The GitHub repository contains the SDK assets, but the actual XeSS code remains closed. This decision may disappoint developers who wanted deeper access to customize the technology for their specific needs.
The latest news regarding the Intel XeSS 2 SDK is that Intel has officially released it, making it more accessible for game developers to integrate their AI-powered upscaling technology into games.
Here are the key takeaways:
- SDK Release: Intel released the XeSS 2.0.1 SDK on GitHub in March 2025. This SDK includes features like XeSS Super Resolution (XeSS-SR), XeSS Frame Generation (XeSS-FG), and Xe Low Latency (XeLL).
- Frame Generation and Low Latency: XeSS 2 introduces Frame Generation (XeSS-FG) for smoother gameplay and Xe Low Latency (XeLL) to minimize input lag, aiming to compete directly with technologies like NVIDIA’s DLSS and AMD’s FSR.
- Game Adoption: Since its release, XeSS 2 has seen adoption in more titles, with Intel announcing in early May 2025 that XeSS (overall) now surpasses 200 games, and XeSS 2 is supported in 19 titles. Notable games gaining XeSS 2 support include Assassin’s Creed: Shadows, Civilization VII, Naraka Bladepoint, and Diablo IV, which has seen significant performance boosts.
- Hardware Compatibility: While XeSS 2 technologies run most efficiently on Intel Arc A- and B-series GPUs and Intel Core Ultra processors (Series 2) with built-in Intel Arc GPUs, XeSS-SR is available for older integrated GPUs and other vendor GPUs supporting SM6.4 (DP4A).
- Developer Tools: Intel has also provided ready-made plugins for Unreal Engine (4 and 5) and Unity, along with updated programming guides and the XeSS Inspector tool for debugging.
- Closed-Source Nature: Despite being available on GitHub, the XeSS SDK remains closed-source, meaning developers are restricted to its binary releases. This has been a point of discussion among the community.
In essence, Intel is pushing to make XeSS 2 a more viable and competitive upscaling solution for PC gaming, with an emphasis on performance improvements and developer integration.
Key Takeaways
- Intel’s XeSS 2.0.1 SDK provides AI-based upscaling to boost game performance while maintaining visual quality.
- The SDK supports multiple game engines but keeps its core upscaling algorithms as closed-source precompiled libraries.
- Developers can implement XeSS-SR, XeSS-FG, and XeLL features through the SDK despite not having access to the underlying code.
Intel XeSS 2 SDK Overview
Intel’s XeSS 2 SDK brings AI-powered upscaling technology to game developers with a set of tools designed to boost frame rates while maintaining visual quality. Despite some expectations, it appears the SDK remains closed-source based on recent releases.
What is Intel XeSS?
XeSS (Xe Super Sampling) is Intel’s AI-based upscaling technology that enhances gaming performance on compatible hardware. The XeSS 2 SDK offers developers access to several key features including XeSS-SR (Super Resolution) and XeSS-FG (Frame Generation).
The technology works by rendering games at a lower resolution and then using AI algorithms to upscale the image to a higher resolution. This process significantly reduces the performance cost while delivering visual quality close to native resolution.
Unlike earlier versions, XeSS 2 introduces frame generation capabilities, which can create intermediate frames to further boost perceived performance. This technology is included in the SDK 2.0.1 release now available to developers.
The SDK supports various platforms and game engines, including Unity and Unreal Engine 4/5, making it accessible to a wide range of development teams.
XeSS vs DLSS and FSR
Intel’s XeSS competes directly with NVIDIA’s DLSS (Deep Learning Super Sampling) and AMD’s FSR (FidelityFX Super Resolution) technologies. Each solution aims to improve gaming performance through upscaling, but they use different approaches.
DLSS relies on NVIDIA’s proprietary hardware and closed algorithms, making it exclusive to RTX graphics cards. FSR takes a more open approach, functioning across multiple GPU brands but with potentially different quality results.
XeSS occupies a middle ground. It performs best on Intel Arc GPUs using specialized XMX AI acceleration hardware, but also works on other GPUs from AMD and NVIDIA through fallback methods using DP4a instructions.
In terms of image quality, XeSS 2 has improved over its predecessor, closing the gap with DLSS while offering broader hardware compatibility than NVIDIA’s solution. However, unlike AMD’s FSR which is fully open source, XeSS 2 SDK still delivers its algorithms as precompiled libraries.
Impact on Game Developers and Graphics Industry
The XeSS 2 SDK offers developers a more streamlined integration process compared to previous versions. This simplification could lead to wider adoption in future game titles, giving players more options for performance optimization.
For game studios, supporting multiple upscaling technologies (DLSS, FSR, and XeSS) has become increasingly important. Each technology offers advantages depending on the player’s hardware, and supporting all three provides the best experience across different GPU brands.
The competition between these technologies drives innovation. Intel’s entry challenges the established players, potentially accelerating improvements in AI-based graphics technologies.
However, the closed-source nature of XeSS 2 may limit community contributions and customizations that could otherwise extend its capabilities. This contrasts with AMD’s approach of making FSR completely open.
For the graphics industry as a whole, these AI upscaling technologies are reshaping expectations about the balance between visual quality and performance, making high-resolution gaming more accessible on mid-range hardware.
Technical Details and Integration
Intel’s XeSS 2 SDK provides developers with powerful tools for implementing AI-enhanced upscaling and frame generation in modern games. The SDK includes several components that work together to deliver improved performance and visual quality across compatible hardware.
Integration with Game Engines
The XeSS 2 SDK supports major game engines including Unity and Unreal Engine 4/5. Developers can add XeSS functionality to their projects through simple API calls and pre-built plugins.
Integration requires minimal code changes for basic implementation. The SDK provides sample code and documentation to help developers get started quickly. For Unity developers, XeSS components can be added directly to camera objects. In Unreal Engine, the process involves adding post-processing elements to the rendering pipeline.
Both DirectX and Vulkan APIs are supported, giving developers flexibility in their graphics implementation. The latest SDK version (2.0.1) includes improved error handling and better compatibility with existing anti-aliasing solutions.
Supported Rendering APIs:
- DirectX 11/12
- Vulkan
XESS SDK in Graphics Development
The XeSS 2 SDK provides three main features: XeSS-SR (Super Resolution), XeSS-FG (Frame Generation), and XeLL (Low Latency). Each component can be implemented separately or combined for maximum benefit.
XeSS-SR uses AI to upscale lower-resolution images to higher resolutions with minimal quality loss. This helps boost performance while maintaining visual quality. The technology works alongside native anti-aliasing solutions.
Frame Generation creates intermediate frames to increase perceived smoothness. This can effectively double framerate in supported games.
Key XeSS 2 Components:
• Super Resolution (SR) - AI upscaling
• Frame Generation (FG) - Creates intermediate frames
• XeLL - Reduces input latency
The SDK includes binary assets rather than open-source code. This approach protects Intel’s proprietary algorithms while still allowing wide adoption.
Hardware Requirements and Optimization
XeSS 2 is optimized for Intel Arc GPUs and newer integrated graphics. These chips contain dedicated XMX (Xe Matrix Extensions) hardware that accelerates AI workloads for maximum performance and quality.
For non-Intel hardware, the SDK offers a DP4A fallback path. This allows AMD and NVIDIA GPUs with Shader Model 6.4 support to run XeSS, though at lower quality and performance than native XMX hardware.
Memory requirements vary based on resolution and features enabled. Super Resolution typically needs 1-2GB of VRAM, while Frame Generation requires additional buffer space.
Developers can fine-tune settings for different hardware configurations. The SDK includes profiling tools to help optimize performance across various GPUs. Intel recommends starting with default quality settings and adjusting based on target hardware profiles.
Frequently Asked Questions
The XeSS SDK provides several tools for developers to enhance game and application visuals. Many developers have specific questions about implementation details, hardware requirements, and compatibility options.
How can developers integrate Intel’s XeSS with their existing projects?
Developers can integrate Intel XeSS into existing projects through the SDK, which includes plugins for popular game engines. The integration process requires adding the XeSS library to the rendering pipeline.
For Unity developers, the process involves importing the XeSS package and configuring it within the post-processing stack. Unreal Engine users can access XeSS through the plugin marketplace.
The SDK provides sample code and implementation guides to help streamline the integration process. Most developers report completing basic integration within a few days.
What are the performance benchmarks for games and applications using Intel XeSS?
XeSS technology typically delivers 30-40% performance gains when upscaling from 1080p to 4K resolutions. The quality mode offers visuals comparable to native resolution with a 20-25% performance improvement.
Games with complex scenes and detailed textures show the most noticeable benefits. Titles like racing simulations and open-world games often see the largest performance boosts.
The performance impact varies based on the selected quality preset and the specific hardware configuration. Intel Arc GPUs show the best results due to XMX acceleration.
Are there any specific system requirements for implementing Intel’s XeSS technology?
XeSS works best on systems with Intel Arc GPUs featuring dedicated XMX matrix engines. These provide hardware acceleration for the AI upscaling algorithms.
The technology also functions on other GPUs through a fallback DP4a path, though with reduced performance. Minimum requirements include DirectX 12 support and at least 6GB of video memory.
Developers should allocate additional memory for the XeSS buffers in their rendering pipeline. The SDK itself requires minimal disk space at under 500MB.
Which platforms support the Intel XeSS SDK and how is it utilized?
The XeSS SDK primarily targets Windows PC platforms with DirectX 12 support. Integration with Vulkan is available but still maturing with each SDK release.
Console support remains unavailable, limiting XeSS to PC gaming. Linux support exists through compatibility layers, though with some performance compromises.
Mobile platforms are not currently supported due to power and thermal constraints. The SDK is utilized through API calls integrated into the game’s rendering pipeline.
What documentation and resources are available for Intel XeSS SDK implementation?
Intel provides comprehensive documentation including integration guides, API references, and best practices. The documentation covers implementation details for both Unity and Unreal Engine.
Sample projects demonstrate practical usage in real-world scenarios. These include code examples for handling different quality presets and fallback options.
Developer forums and support channels offer direct assistance for implementation challenges. Intel also maintains tutorial videos explaining key concepts and integration steps.
Can Intel XeSS be used in tandem with non-Intel hardware, and if so, are there any limitations?
XeSS works on non-Intel hardware through the DP4a fallback path, making it compatible with NVIDIA and AMD GPUs. This universal support helps developers reach a wider audience.
Performance on non-Intel hardware is typically 10-15% lower than on equivalent Intel Arc GPUs. The quality difference is minimal but noticeable in side-by-side comparisons.
Some advanced features like adaptive quality scaling work best on Intel hardware. Developers should test across multiple hardware configurations to ensure consistent performance and visual quality.







