Intel’s latest Core Ultra 9 285K processor has made waves in the tech world with its impressive performance at low power – but that seems to be mostly in single threaded applications. The new chip outpaces its predecessor, the i9-14900K, by up to 13% in Cinebench R23 multi-core tests. But despite this improvement, the Core Ultra 9 285K still lags behind AMD’s Ryzen 9 9950X in multi-threaded performance at nearly 111W more power.
The Core Ultra 9 285K scored 46,289 points in Cinebench R23 at 364W power consumption. In contrast, the Ryzen 9 9950X achieved better results at lower power levels. AMD’s chip performed well at both 253W and 230W settings, highlighting its efficiency advantage.

Intel’s new processor shows promise in single-core tasks. But for users who need top-tier multi-threaded performance, AMD’s Ryzen 9 9950X remains the stronger choice. The battle between these two chips showcases the ongoing competition in the CPU market.
Unpacking the Intel Core Ultra 9 285K vs. AMD Ryzen 9 9950X Performance Puzzle
The tech world is buzzing with the arrival of Intel’s Core Ultra 9 285K, the first processor in their new line. While it boasts impressive single-threaded performance, some benchmarks reveal a surprising twist: the 285K seems to lag behind the AMD Ryzen 9 9950X in multi-threaded scenarios. Let’s dive deeper into this unexpected outcome.
Single-Threaded Supremacy: A New Champion Emerges
The Core Ultra 9 285K, built on Intel’s innovative architecture, showcases a significant leap in single-threaded performance. This is excellent news for tasks that rely heavily on single-core speeds, such as gaming and everyday applications. It demonstrates Intel’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of individual core performance.
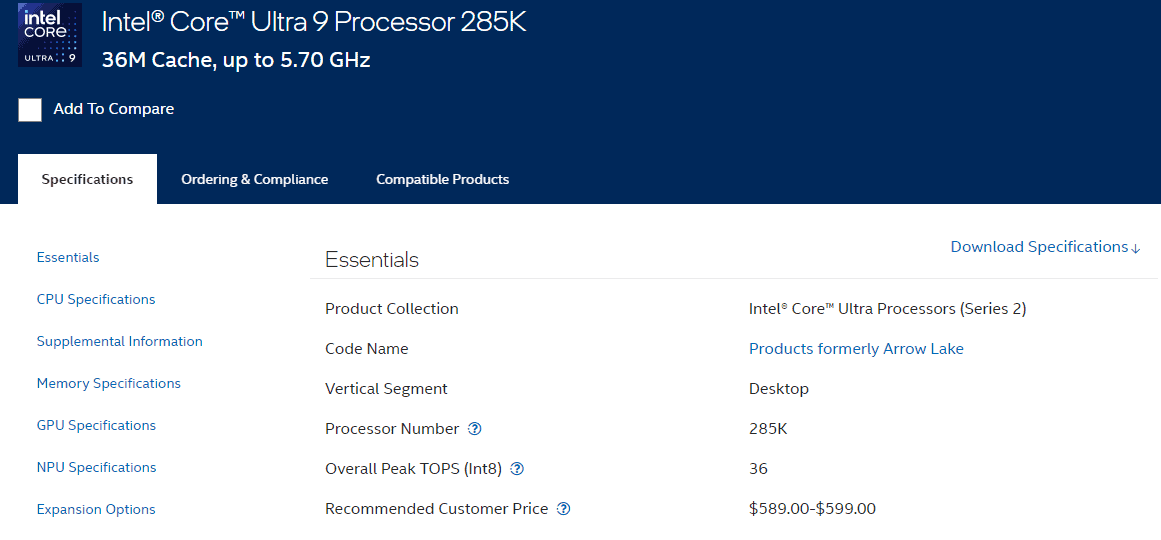
Multi-Threaded Matchup: Where the 9950X Takes the Lead
Despite its single-threaded prowess, the 285K appears to fall short in multi-threaded benchmarks. The Ryzen 9 9950X, with its higher core count and hyperthreading capabilities, often emerges as the victor in these tests. This disparity is particularly noticeable in heavily threaded applications like video editing, 3D rendering, and scientific simulations.
Breaking Down the Performance Discrepancy
Several factors contribute to the 285K’s multi-threaded performance gap:
- Hyperthreading: The 9950X leverages hyperthreading, allowing each core to handle multiple threads simultaneously. The 285K lacks this feature, limiting its multi-threaded capabilities.
- Core Count: The 9950X boasts a higher core count than the 285K, providing more processing power for multi-threaded workloads.
- AVX-512 Implementation: Some benchmarks utilize AVX-512 instructions, which may be more efficiently implemented on AMD’s Zen 4 architecture compared to the 285K. This could contribute to the 9950X’s advantage in certain tests.

Beyond the Benchmarks: Real-World Considerations
While benchmarks offer valuable insights, it’s essential to consider real-world usage scenarios. For many users, the 285K’s exceptional single-threaded performance will translate to a smoother and more responsive computing experience. However, for power users who frequently engage in heavily threaded tasks, the 9950X might be the more suitable choice.
The Power Consumption Equation
Early indications suggest that the 285K might have higher power consumption than the 9950X. This factor could influence users concerned about energy efficiency and heat generation, particularly those with smaller form factor systems or limited cooling solutions.
Price and Availability: A Crucial Factor
The Core Ultra 9 285K is positioned as a high-end CPU, and its price will play a significant role in its overall value proposition compared to the 9950X. Consumers will need to weigh the performance benefits against the cost to determine the best option for their needs and budget.
Key Differences: Intel Core Ultra 9 285K vs. AMD Ryzen 9 9950X
| Feature | Intel Core Ultra 9 285K | AMD Ryzen 9 9950X |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Intel “Arrow Lake” | AMD “Zen 4” |
| Cores/Threads | (Information not yet released) | 16 cores / 32 threads |
| Base Clock Speed | (Information not yet released) | (Information not yet released) |
| Boost Clock Speed | (Information not yet released) | (Information not yet released) |
| Hyperthreading | No | Yes |
| L3 Cache | (Information not yet released) | 32MB |
| TDP | (Information not yet released) | 170W |
| Single-threaded Performance | Generally higher | Generally lower |
| Multi-threaded Performance | Generally lower | Generally higher |
Community Insights: Why Choose the 285K?
A recent Reddit thread on r/pcmasterrace sparked a lively debate about the Intel Core Ultra 9 285K’s value proposition compared to the AMD Ryzen 9 9950X. While many users highlighted the 9950X’s multi-threaded advantage, several compelling arguments emerged in favor of the 285K:
- QuickSync: Intel’s QuickSync technology offers hardware-accelerated video encoding and decoding, which can be a significant advantage for content creators and streamers.
- Thunderbolt Support: Intel CPUs often provide better support for Thunderbolt connectivity, offering high-speed data transfer and daisy-chaining capabilities.
- Specific Use Cases: Some users emphasized that the 285K’s single-threaded performance might be preferable for specific applications or older games that rely heavily on single-core speeds.
- Brand Loyalty and Familiarity: A few users mentioned that some individuals might simply prefer Intel due to brand loyalty or familiarity with their platforms.
It’s worth noting that several users also pointed out the 285K’s potentially higher power consumption as a drawback. However, the thread highlighted that the extreme power consumption figures were associated with an optional “Extreme Mode” and that the 285K could operate at lower power levels with comparable performance to the 9950X.
This discussion underscores the importance of considering individual needs and priorities when choosing a CPU. While the 9950X might excel in multi-threaded tasks, the 285K offers unique advantages that could be decisive for certain users.
Key Takeaways
- Intel’s Core Ultra 9 285K surpasses the i9-14900K but falls short of AMD’s Ryzen 9 9950X
- The Ryzen 9 9950X offers better multi-threaded performance at lower power consumption
- CPU choice depends on specific user needs and workloads
Intel Core Ultra 285K vs. AMD Ryzen 9 9950X: A Comparative Analysis
The Intel Core Ultra 285K and AMD Ryzen 9 9950X are top-tier desktop CPUs. They offer high performance for demanding tasks and gaming. Their specs and benchmarks reveal key differences in processing power and efficiency.
Performance Overview and Benchmarks
The AMD Ryzen 9 9950X outperforms the Intel Core Ultra 9 285K in multi-threaded tasks. Benchmark results show the 9950X is about 13% faster in multi-core tests. This edge makes it better for heavy workloads like video editing and 3D rendering.
The Intel chip takes the lead in single-core performance. It’s roughly 8% faster in single-threaded tasks. This advantage can benefit some games and lighter applications.
In Cinebench R23, the 9950X scores higher due to its superior multi-core strength. The Core Ultra 285K shows competitive results in single-core tests.
Gaming performance varies by title. Some games favor Intel’s single-core speed, while others benefit from AMD’s extra threads.
Technological Specifications and Features
The Core Ultra 9 285K boasts 24 cores and 24 threads. It uses a mix of performance and efficiency cores. The base clock is 3.7 GHz, with boost speeds reaching higher frequencies.
AMD’s Ryzen 9 9950X features 16 cores and 32 threads. All cores are high-performance. Its base clock is 4.3 GHz, with boost clocks up to 5.7 GHz.
Both CPUs support DDR5 memory. The 9950X has a higher TDP at 170W compared to the 285K’s lower power draw.
Intel’s chip includes an AI accelerator. This feature may boost performance in AI-enhanced tasks.
The 285K uses the new LGA 1851 socket. AMD’s 9950X is compatible with existing AM5 motherboards.
Pricing favors Intel slightly. The Core Ultra 9 285K costs about $50 less than the Ryzen 9 9950X at launch.







