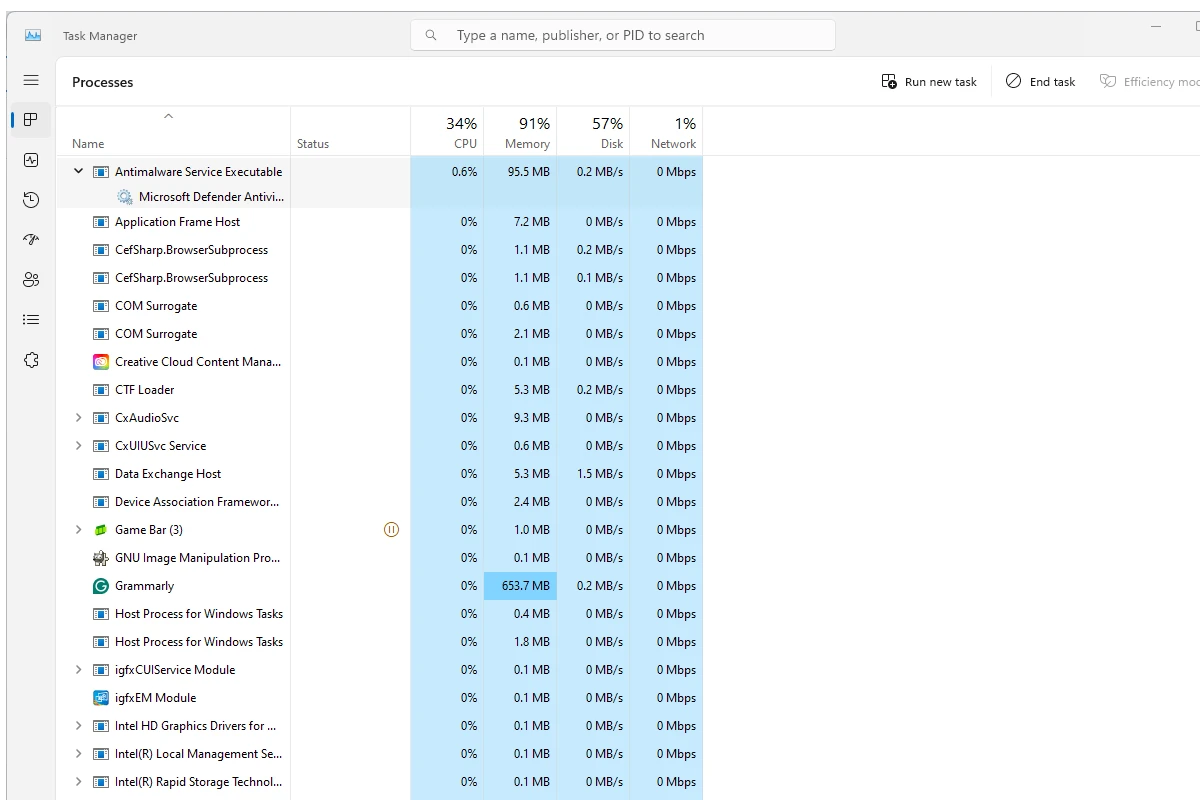
The Antimalware Service Executable is a process in Windows that helps protect your computer from threats. It’s part of Windows Defender, the built-in security tool. Sometimes this process uses a lot of memory, which can slow down your PC. High memory usage by Antimalware Service Executable can slow down your computer and make it harder to get work done. But with a little troubleshooting, you can improve its performance and keep your system secure.
This guide offers insights into the causes of high memory usage, effective solutions, and additional tips for managing resource consumption. You can reduce high memory usage by turning off real-time protection temporarily or changing scan settings, which can help your computer run faster. Just be careful – turning off protection can leave your PC open to viruses. There are other ways to lower memory use as well. You can add files to an exclusion list or change when scans happen. These tricks can help your PC work better without sacrificing safety.

Antimalware Service Executable: A Guide to Tackling High Memory Usage
Understanding Antimalware Service Executable
Antimalware Service Executable, or MsMpEng.exe, is a core component of Windows Defender, your built-in antivirus protection. It safeguards your system by scanning files and processes for potential threats. However, it can sometimes consume excessive memory, impacting your system’s performance.
Common Causes of High Memory Usage
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Full System Scans | During scheduled or manual full scans, Antimalware Service Executable utilizes more resources to thoroughly check your entire system. |
| Real-time Protection | This feature actively monitors file activity, leading to increased memory usage during file downloads, installations, or accesses. |
| Large File Scans | Scanning large files or numerous files simultaneously can strain memory resources. |
| Malware Infections | Active malware infections can trigger Antimalware Service Executable to work harder, consuming more memory. |
| Outdated Software | Outdated Windows Defender definitions or an outdated operating system can contribute to performance issues. |
Troubleshooting Steps
- Check for Malware: Run a full system scan using Windows Defender or a reputable third-party antivirus tool to eliminate any potential threats.
- Schedule Scans During Idle Time: Configure Windows Defender to perform scans during periods when you’re not actively using your computer to minimize performance impact.
- Exclude Files and Folders: Add specific files, folders, or processes to Windows Defender’s exclusion list to prevent unnecessary scanning and reduce resource usage.
- Update Windows Defender and Windows: Ensure that both Windows Defender and your operating system are up-to-date with the latest definitions and security patches.
- Consider a Third-Party Antivirus: If Windows Defender consistently causes performance issues, explore alternative antivirus solutions that may be more efficient.
- Optimize System Settings: Adjust Windows Defender’s settings to prioritize performance over maximum protection if you trust your online habits and have other security measures in place.
Additional Tips
- Monitor Resource Usage: Use the Task Manager to keep an eye on Antimalware Service Executable’s resource consumption and identify potential triggers for high memory usage.
- Restart Your Computer: Sometimes a simple restart can resolve temporary glitches and optimize system performance.
- Seek Professional Help: If the issue persists, consider contacting Microsoft support or a qualified technician for further assistance.
Key Takeaways
- Antimalware Service Executable is a Windows Defender process that can use lots of memory
- Turning off real-time protection can help, but may risk computer safety
- Changing scan settings or adding exclusions can reduce memory use while keeping protection
Understanding Antimalware Service Executable
Antimalware Service Executable is a key part of Windows security. It helps protect computers from viruses and other bad software. This program uses memory and CPU power to keep systems safe.
Role in Windows Security
Antimalware Service Executable, also known as MsMpEng.exe, is the main part of Microsoft Defender. It runs in the background on Windows 10 and 11 computers. This program looks for viruses, spyware, and other threats.
It checks files when you open them. It also scans your whole computer at set times. Microsoft Defender is always working to keep your system safe.
This tool is part of Windows Security. It’s free and built into Windows, so you don’t need to buy extra antivirus software.
Common Issues with Memory and CPU Usage
Sometimes Antimalware Service Executable uses a lot of memory or CPU power. This can slow down your computer. You might see high usage in Task Manager.
There are a few reasons this can happen:
- Full system scans
- Checking many files at once
- Updates to the virus database
If your computer slows down, you can try these fixes:
- Run a manual scan
- Update Windows
- Check for conflicts with other antivirus programs
Most of the time, high usage is short-term. It often goes back to normal on its own.

Impact of Real-Time Protection
Real-time protection is a key feature of Antimalware Service Executable. It checks files as soon as you open them. This helps catch viruses right away.
But real-time protection can use up system resources. It might make your computer run slower. Some people turn it off to speed up their system.
Turning off real-time protection can be risky. It leaves your computer open to new threats. If you do turn it off, only do so for a short time. Remember to turn it back on to stay safe.
You can manage real-time protection in Windows Security settings. Finding the right balance between safety and speed is important.