There are rumors circling that Intel may be a target for acquisition, with Qualcomm showing interest as a potential buyer. Obviously there would be significant regulatory and national security hurdles that would need to be worked out for this to have any legs, but it is an indication of how far the once-mighty chipmaker (Intel) has fallen; given that a one-time smaller competitor is now considering purchasing them outright.
Despite the lack of details regarding the potential price for Intel and what the combined enterprise would look like, if this acquisition were to happen, it could significantly impact the tech industry and give Qualcomm a dominant position in various sectors. Analysts are speculating about the potential implications of this move, and we’ll have to take a wait-and-see approach to the news. Either way, the outcome of these talks could provide insight into the future of chip-making in the tech industry and could seriously shake up the tech-hardware and chip-making world.

A Chip Industry Shakeup? Qualcomm Eyes Intel Acquisition
The Potential Deal
Whispers in the tech world suggest that Qualcomm, the mobile chip giant, has expressed interest in a potential takeover of Intel, the veteran of the semiconductor industry. The news sent ripples through the market, with Intel’s stock experiencing a surge while Qualcomm’s saw a slight dip.
The Strategic Fit
- Qualcomm, renowned for its dominance in smartphone chips, could gain a foothold in the PC and data center markets through Intel’s established presence.
- Intel, grappling with manufacturing challenges and the booming AI sector dominated by Nvidia, might find stability and a strategic partner in Qualcomm.
- The combined entity could possess the scale and resources to challenge other industry giants, accelerating innovation and expanding market reach.
Challenges and Uncertainties
- The deal is far from certain, with regulatory hurdles and potential cultural clashes to overcome.
- The sheer size and complexity of both companies could make integration a daunting task.
- The acquisition, if successful, could reshape the entire semiconductor landscape, impacting competitors, suppliers, and customers alike.
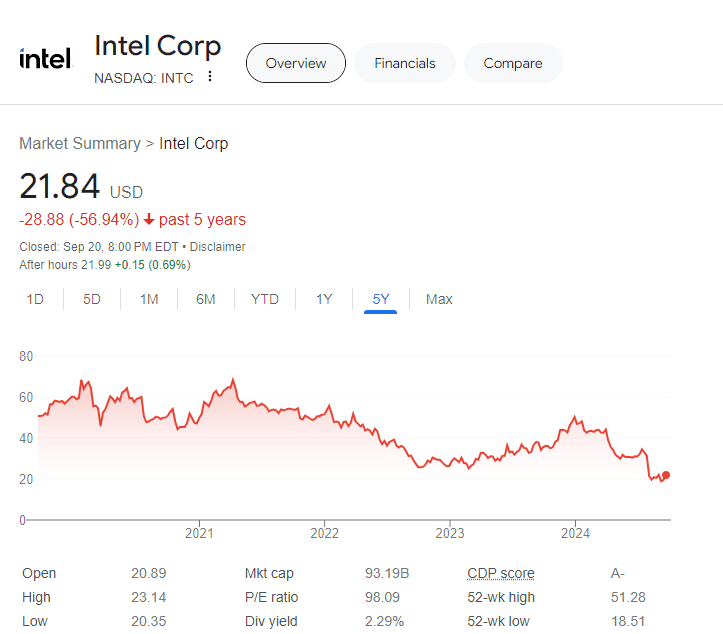
Table: Potential Impacts of a Qualcomm-Intel Merger
| Area | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Market Share | Increased market power in various segments, including smartphones, PCs, and data centers. |
| Innovation | Combined R&D resources could accelerate technological advancements, particularly in 5G and AI. |
| Competition | Could create a formidable rival for other chipmakers like Nvidia, AMD, and TSMC. |
| Jobs | Potential job cuts and restructuring as the companies streamline operations. |
| Consumer Prices | Could lead to higher prices for consumers due to decreased competition. |
The potential takeover of Intel by Qualcomm has ignited discussions about the future of the semiconductor industry. While the deal faces significant hurdles, its success could reshape the competitive landscape and drive innovation in key areas like AI and 5G. The industry watches with bated breath as this story unfolds, its outcome poised to influence the future of technology for years to come.
Short Summary:
- Qualcomm is actively exploring a potential acquisition of Intel.
- The negotiations are reportedly in the early stages, with no formal offer made yet.
- A potential merger would raise substantial antitrust concerns and regulatory scrutiny.

In an intriguing development, Qualcomm Inc. has purportedly initiated discussions with Intel Corp. regarding a possible acquisition. The news was first reported by the Wall Street Journal and later confirmed by sources familiar with the matter, indicating that Qualcomm’s CEO, Cristiano Amon, is closely engaged in these talks. Although the negotiations are in their infancy, they suggest a significant shift in the technology sector, particularly as both companies navigate different challenges in the competitive semiconductor industry.
Intel, once hailed as the titan of chip manufacturing, has faced a myriad of challenges that have drastically impacted its market valuation. As of late, the company’s shares have plummeted nearly 60% this year alone, leading to widespread skepticism regarding its operational direction and future sustainability. In contrast, Qualcomm stands as a formidable player in mobile chip design, though it lacks direct manufacturing capabilities, relying instead on third-party organizations such as Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co. (TSMC).
“Qualcomm’s interest in Intel is indicative of the shifting dynamics in the semiconductor landscape, where traditional powerhouses are reevaluating their positions,” noted an anonymous industry analyst.
The proposition of a Qualcomm-Intel alliance raises numerous questions, particularly relating to financial logistics and regulatory hurdles. With Intel’s market capitalization hovering around $122 billion—reflecting its debts—analysts are left to ponder how Qualcomm, valued at about $188 billion, would finance such a substantial takeover, especially considering its available cash reserves, which amount to approximately $13 billion.
Current Context:
Qualcomm’s approach arrives at a pivotal moment for Intel, which has seen its glory dimmed in recent years. Although its traditional dominance in eras past was cemented largely due to its x86 architecture, competitors have begun to encroach on its territory. AMD has emerged as a significant rival, and Nvidia has dominated the graphics processing segment crucial for AI applications, something Intel has recently struggled with.
In a memo released to employees following a board meeting, Intel’s CEO, Pat Gelsinger, reaffirmed the company’s direction towards strengthening its manufacturing avenues. The memo highlighted a commitment to invest heavily in Intel’s foundry business, with projections suggesting it would require a staggering $100 billion over the next five years to regain footing in the semiconductor race.
“Intel is at a crossroads; it needs drastic transformation to come back from its operational setbacks,” remarked another industry insider.
The Competitive Landscape:
Both Qualcomm and Intel operate in overlapping areas of the semiconductor market, predominantly in chips for personal computers and laptops. The intriguing twist, however, is that Qualcomm does not manufacture its chips, relying instead on contract manufacturers to produce its designs. This strategic difference may complicate any potential acquisition, especially as Qualcomm would need to manage the complexities of Intel’s manufacturing processes, which require advanced technology and significant investment. Unlike Qualcomm, Intel has developed expertise in chip fabrication, amassing a workforce that has dedicated years to perfecting production methodologies.
Market Reactions:
As news of Qualcomm’s interest in Intel emerged, market responses were mixed. Shares of Intel experienced a modest uptick of 3.3%, closing at approximately $21.87, while Qualcomm’s stock fell by 2.9%. Despite the fluctuations, analysts noted that a serious acquisition approach could inevitably stimulate volatility in the sector. Qualcomm’s shares have slipped, reflecting investor concern regarding the risks associated with a move of this magnitude.
Regulatory and Antitrust Challenges:
Should Qualcomm proceed with a formal offer, the transaction would likely garner significant scrutiny from regulatory bodies across the United States, Europe, and China. Both companies previously experienced roadblocks in their respective negotiations, highlighting the complications posed by international business. Qualcomm’s aborted attempt to merge with NXP Semiconductors and Intel’s failed acquisition of Tower Semiconductor serve as reminders of the hurdles that acquisitions can face.
“With both companies maintaining operations in China, regulatory constraints can introduce substantial delays,” stated a former government official involved in antitrust matters.
In addition, if regulators approve the acquisition, Qualcomm might have to sell parts of Intel to address antitrust concerns. Such requirements could change the terms and feasibility of any potential merger. As Qualcomm continues to explore its options, there are broader implications to consider for both chipset firms and the semiconductor industry. The pursuit of innovations, especially in artificial intelligence and advanced computing technology, is now more important than ever. Intel’s recent struggles to keep up with AI-driven market advancements, including its failure to gain significant shares of AI processing, have made it susceptible to changes in consumer preferences.
Breakdown Of The Companies
Who is Intel?
Intel is a major American tech company known for making computer chips, especially the ones that power most personal computers. They’ve been around for a long time and are key players in the semiconductor industry, driving innovation in areas like processing power and data centers.
Intel at a Glance
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Founded | 1968 by Robert Noyce and Gordon Moore |
| Headquarters | Santa Clara, California, USA |
| Core Business | Design and manufacture of semiconductors, microprocessors, and other computer components |
| Products | CPUs, GPUs, chipsets, memory, storage, networking solutions, software, etc. |
| Notable Achievements | x86 architecture, microprocessors for personal computers, leading role in the semiconductor industry |
| Current Focus | Expanding beyond PCs to AI, 5G networks, cloud computing, autonomous driving, and more |
Who is Qualcomm?
Qualcomm is another big American tech company that focuses on wireless technology. They’re famous for their Snapdragon chips found in many smartphones, enabling fast internet connections and powerful performance. They also work on other wireless tech like 5G and are always pushing the boundaries of mobile connectivity.
Qualcomm: A Snapshot
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Founded | 1985 by Irwin M. Jacobs and others |
| Headquarters | San Diego, California, USA |
| Core Business | Design and manufacture of wireless communication technologies and semiconductors |
| Products | Mobile processors (Snapdragon), modems, RF front-end components, automotive chips, IoT solutions, etc. |
| Notable Achievements | Pioneering CDMA technology, leading supplier of smartphone chips, driving innovation in 5G and wireless connectivity |
| Current Focus | Expanding into new markets like automotive, IoT, and XR (extended reality) while maintaining leadership in mobile technology |