Do you ever notice rough lines in video games or digital images? These jagged edges can make graphics look less smooth and realistic. That’s where anti-aliasing comes in. It’s a tool used in computer graphics to make edges look smoother. Anti-aliasing is important for gamers because it smooths out jagged edges and improves overall image quality. However, there are different types of anti-aliasing with varying impacts on performance. It’s important to understand the trade-offs and make informed decisions.
Anti-aliasing is a technique that blends pixel colors to create softer edges in digital images and games. It works by calculating the average color values around edges. This helps remove the stair-step look often seen on diagonal lines in digital graphics.
There are different types of anti-aliasing. Each method has its own way of smoothing edges. Some are better for image quality while others are faster for computers to process. Supersampling is one basic type that uses higher resolution images. Other methods like multi-sampling focus on specific parts of an image. The right choice depends on what you need for your graphics or games.
Unveiling Anti-Aliasing: A Gamer’s Guide
What is Anti-Aliasing?
Anti-aliasing (AA) is a technique used in computer graphics to smooth out jagged edges, also known as “jaggies,” that can appear on objects and lines, particularly those at an angle or curve. These jaggies are a result of the limited resolution of displays, where pixels try to represent smooth lines with their blocky shapes. AA works by blending the colors of pixels along these edges, creating a smoother and more visually pleasing image.
Types of Anti-Aliasing
Several types of anti-aliasing techniques are available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
- MSAA (Multisample Anti-Aliasing): One of the oldest and most common AA methods, it supersamples pixels along edges to create a smoother appearance. It can be quite effective but can also be demanding on your GPU.
- FXAA (Fast Approximate Anti-Aliasing): A post-processing technique that applies a blur filter to smooth out jaggies. It’s less demanding on your system but can lead to a slightly blurry image overall.
- TAA (Temporal Anti-Aliasing): A more modern technique that combines information from multiple frames to smooth out edges over time. It can provide excellent results with less performance impact than MSAA, but it can also introduce some visual artifacts like ghosting.
- DLSS (Deep Learning Super Sampling): An AI-powered technique exclusive to NVIDIA GPUs that uses deep learning to upscale lower-resolution images, providing both improved performance and image quality.
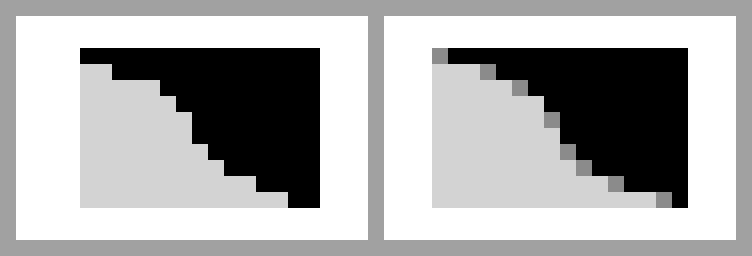
Image Credit: Reff Pixels, CC BY-SA 4.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Should You Turn It On or Off?
The decision to enable or disable anti-aliasing depends on a few factors:
- Your visual preferences: If you’re sensitive to jaggies and prioritize image quality, then turning on AA is recommended.
- Your hardware: More demanding AA techniques like MSAA can impact performance, especially on older or lower-end systems. You might need to experiment with different settings to find the right balance between visuals and frame rate.
- The game itself: Some games might look better with certain AA methods, while others might not benefit as much. It’s worth checking online or in-game settings to see if there are any recommendations.
Comparing Anti-Aliasing Techniques
| Technique | Image Quality | Performance Impact | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| MSAA | High | High | Can be demanding on your GPU. |
| FXAA | Moderate | Low | Can lead to a slightly blurry image. |
| TAA | High | Moderate | Can introduce ghosting artifacts. |
| DLSS | High | Low (on compatible NVIDIA GPUs) | Requires an RTX GPU. |
Understanding Anti-Aliasing
Anti-aliasing helps make images look smoother on screens. It fixes jagged edges that can appear in games and other graphics. Let’s look at how it works and why it matters.
Basics of Pixels and Aliasing
Screens show images using tiny squares called pixels. Each pixel can only be one color at a time. This can cause problems when showing curved or slanted lines. These lines can look jagged or stair-like. This effect is called aliasing.
Aliasing happens most often in games and 3D graphics. It makes edges look rough instead of smooth. Jagged edges can make images less pretty to look at. They can also make it harder to see small details.
Types of Anti-Aliasing
There are many types of anti-aliasing. Each one works a bit differently:
- FXAA: Fast and easy on computers
- MSAA: Good balance of quality and speed
- SSAA: Best quality but needs a strong computer
- TAA: Helps with moving images
SSAA renders images at a higher resolution first. Then it shrinks them down. This makes edges very smooth. But it can slow down games a lot.
MSAA only smooths certain parts of an image. It’s faster than SSAA but still looks good.
How Anti-Aliasing Improves Image Quality
Anti-aliasing makes images look cleaner and more real. It smooths out jagged lines and curves. This can make games and graphics look much better.
With anti-aliasing, text is easier to read. Small objects look clearer. Edges of buildings and characters appear smoother.
Anti-aliasing boosts overall visual quality. It helps images look less pixelated. This is especially helpful on bigger screens or when sitting close to the display.
Some types work better for still images. Others are great for moving pictures in games. Picking the right type can make graphics look amazing without slowing down your computer too much.
Technical Aspects of Anti-Aliasing
Anti-aliasing smooths jagged edges in digital images. It uses different methods to blend pixels and create cleaner graphics. Let’s look at how it affects performance and its role in gaming.
Impact on Performance
Anti-aliasing can slow down a computer. It needs extra processing power from the graphics card. This can lower frame rates in games. Some types of anti-aliasing use more power than others.
Supersampling is very demanding. It renders images at higher resolutions. Then it shrinks them down. This gives great results but uses a lot of power.
Lighter methods like FXAA use less power. They work faster but may not look as good. Gamers often have to choose between smooth edges and fast gameplay.
Modern GPUs can handle anti-aliasing better. They have special hardware for it. This helps reduce the performance hit.
Anti-Aliasing in Gaming and Digital Graphics
Games use anti-aliasing to look more real. It helps create smooth edges on objects and characters. This makes the game world feel more solid.
Different game types need different anti-aliasing. Fast games might use light methods. Slower games can use heavier ones for better looks.
Temporal anti-aliasing is popular in modern games. It uses info from past frames to smooth edges. This works well with moving images.
Digital artists also use anti-aliasing. It helps create crisp logos and clean illustrations. Web designers use it to make sharp text on websites.
Anti-aliasing is key for VR and AR. These need very smooth images to feel real. Good anti-aliasing helps prevent motion sickness in VR.
Frequently Asked Questions
Anti-aliasing helps make games look better. It can affect how well games run. Different types work in different ways. Let’s look at some key questions about anti-aliasing.
How does anti-aliasing improve visual quality in games?
Anti-aliasing smooths jagged edges in games. It blends pixel colors. This makes lines and edges look more natural. The result is a cleaner image.
Games look less pixelated with anti-aliasing. Objects have smoother outlines. This is most clear on diagonal lines and curves.
What are the performance impacts of using anti-aliasing in computer graphics?
Using anti-aliasing can slow down games. It needs extra computer power to work.
Some types of anti-aliasing use more power than others. Stronger anti-aliasing often means lower frame rates. Players may need to balance looks and speed.
What differences exist between various anti-aliasing techniques, such as FXAA and MSAA?
FXAA is fast but can blur textures. MSAA gives better quality but uses more power.
TAA samples pixels over time. This can give good results with less impact on speed. Each method has its own pros and cons.
Can anti-aliasing cause latency issues in fast-paced games?
Some anti-aliasing can add a tiny delay. This is usually too small to notice.
In very fast games some players turn it off. They prefer speed over looks. Most gamers don’t have issues with latency from anti-aliasing.
How does anti-aliasing interact with frame rate and overall performance?
Anti-aliasing can lower frame rates. More anti-aliasing often means fewer frames per second.
Higher resolutions may need less anti-aliasing. At 4K some games look smooth without it. Players can adjust settings to find the right balance.
What considerations should be taken when deciding to enable or disable anti-aliasing?
Think about your computer’s power. Check how the game looks with it on and off.
Consider your monitor size and resolution. Bigger screens may show more jagged edges. Higher resolutions might need less anti-aliasing. Try different settings to see what works best.