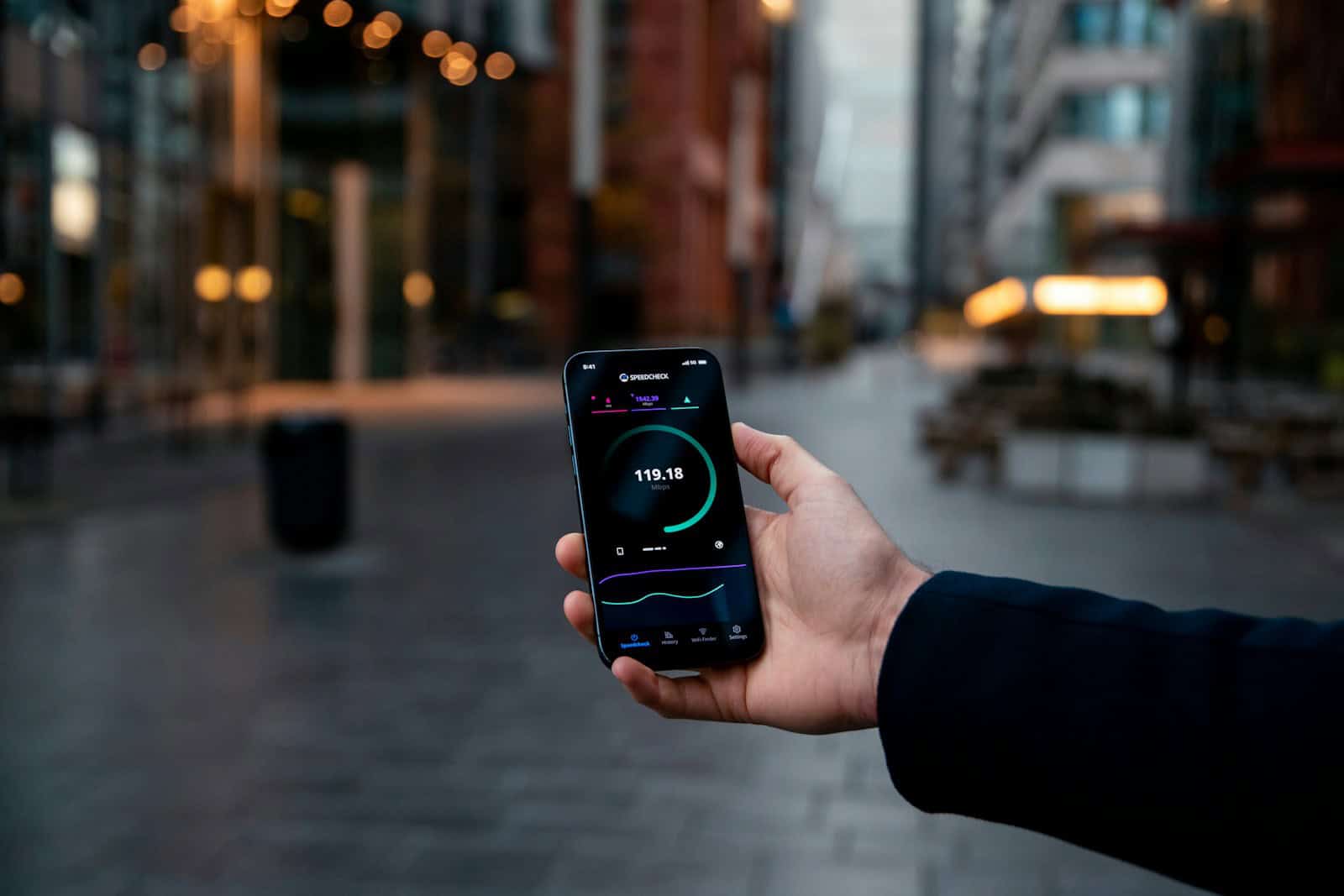
Transmission speed plays a critical role in how effectively we can communicate over computer networks. This speed signifies how quickly data packets can move across a network from one point to another. Measuring transmission speed involves bits per second; the higher the number of bits that can travel per second, the faster the communication.
Understanding network transmission speeds is essential not only for IT professionals but for anyone relying on the internet for work, leisure, or learning. Network speeds can vary widely based on technology and infrastructure. While older network standards like 802.11b offer more modest speeds, newer developments in technology are pushing the boundaries, allowing for gigabit and even terabit speeds under certain conditions.
Optimizing Your Network for Speed and Reliability
Network transmission speeds are crucial for many applications, from streaming high-definition videos to online gaming and video conferencing. Understanding the factors that affect network speeds can help you make informed decisions when choosing a service provider, optimizing your network, and troubleshooting issues.
Factors Affecting Network Transmission Speeds
Network transmission speeds are influenced by various factors, including:
- Bandwidth: The maximum amount of data that can be transmitted over a network connection in a given time. Higher bandwidth generally results in faster speeds.
- Latency: The time it takes for a data packet to travel from the source to the destination. Lower latency is desirable for real-time applications like gaming and video conferencing.
- Network congestion: When too many devices are using the same network, it can lead to slower speeds and increased latency.
- Distance: The physical distance between the sender and receiver can affect transmission speeds, especially for long-distance connections.
- Hardware and software: The quality and configuration of your network equipment, as well as the software you use, can also impact speeds.
Types of Network Connections
Different types of network connections offer varying speeds and capabilities. Some common types include:
- Ethernet: Wired connections that offer high speeds and low latency, ideal for gaming and other demanding applications.
- Wi-Fi: Wireless connections that are convenient but may have lower speeds and higher latency than Ethernet, especially at longer distances or with interference.
- Cellular (4G/5G): Mobile connections that offer increasing speeds and coverage, but may have higher latency and data caps compared to wired or Wi-Fi options.
- Satellite: Used in remote areas where other connections are unavailable, but typically have high latency and lower speeds.
Choosing the Right Network Speed
The ideal network speed for you depends on your specific needs and usage patterns. Consider the following factors:
- Number of users and devices: If you have multiple users or devices on your network, you’ll need higher speeds to ensure everyone has a good experience.
- Types of activities: High-definition streaming, online gaming, and video conferencing require higher speeds than web browsing or email.
- Budget: Higher speeds generally come with higher costs, so consider your budget when choosing a plan.
Optimizing Your Network Speed
To maximize your network speed, you can:
- Upgrade your equipment: Older routers or modems may not be able to handle high speeds. Upgrading to newer models can significantly improve performance.
- Use a wired connection: If possible, connect your devices directly to your router with an Ethernet cable for the fastest and most reliable connection.
- Reduce network congestion: Limit the number of devices using your network at the same time, especially during peak hours.
- Update your software: Ensure your operating system, browser, and other software are up-to-date to take advantage of the latest performance optimizations.
- Check for interference: If you’re using Wi-Fi, make sure there are no obstacles or other devices interfering with the signal.
Troubleshooting Network Speed Issues
If you’re experiencing slow network speeds, try the following steps:
- Restart your modem and router: This can often resolve temporary glitches and improve performance.
- Check your speed: Use an online speed test to verify your actual download and upload speeds.
- Contact your service provider: If your speeds are consistently lower than what you’re paying for, contact your provider for assistance.
- Check for malware: Malicious software can sometimes hog bandwidth and slow down your connection.
Remember, network transmission speeds are a complex issue influenced by many factors. By understanding these factors and taking steps to optimize your network, you can ensure a fast and reliable connection for all your online activities.
Key Takeaways
- Network transmission speed is measured in bits per second.
- Speeds vary depending on the technology and network standard.
- Higher transmission speeds provide quicker communication over networks.
Fundamentals of Network Transmission Speeds
Networks transfer data at various speeds. These speeds are important for the performance of online activities, streaming, or file transfers. Understanding the basics of network transmission speeds helps one grasp how quickly data moves across a network.
The Role of Routers and Access Points
Routers act as traffic directors on a network. They guide data to the correct destination. Access points connect wireless devices to a network. Both routers and access points affect the speed and quality of a network connection.
Wireless Standards and Frequencies
Wireless standards, like IEEE 802.11, set rules for how devices talk to each other. They use different frequencies such as 2.4GHz and 5GHz. The 5GHz frequency is faster but covers less distance. The 2.4GHz frequency covers more area but is slower.
Understanding Bandwidth and Throughput
Bandwidth is how much data can move through a network at one time. It’s like how many lanes a highway has. Throughput is how much data actually moves through. It can be less than the bandwidth due to network interference or how the network is set up.