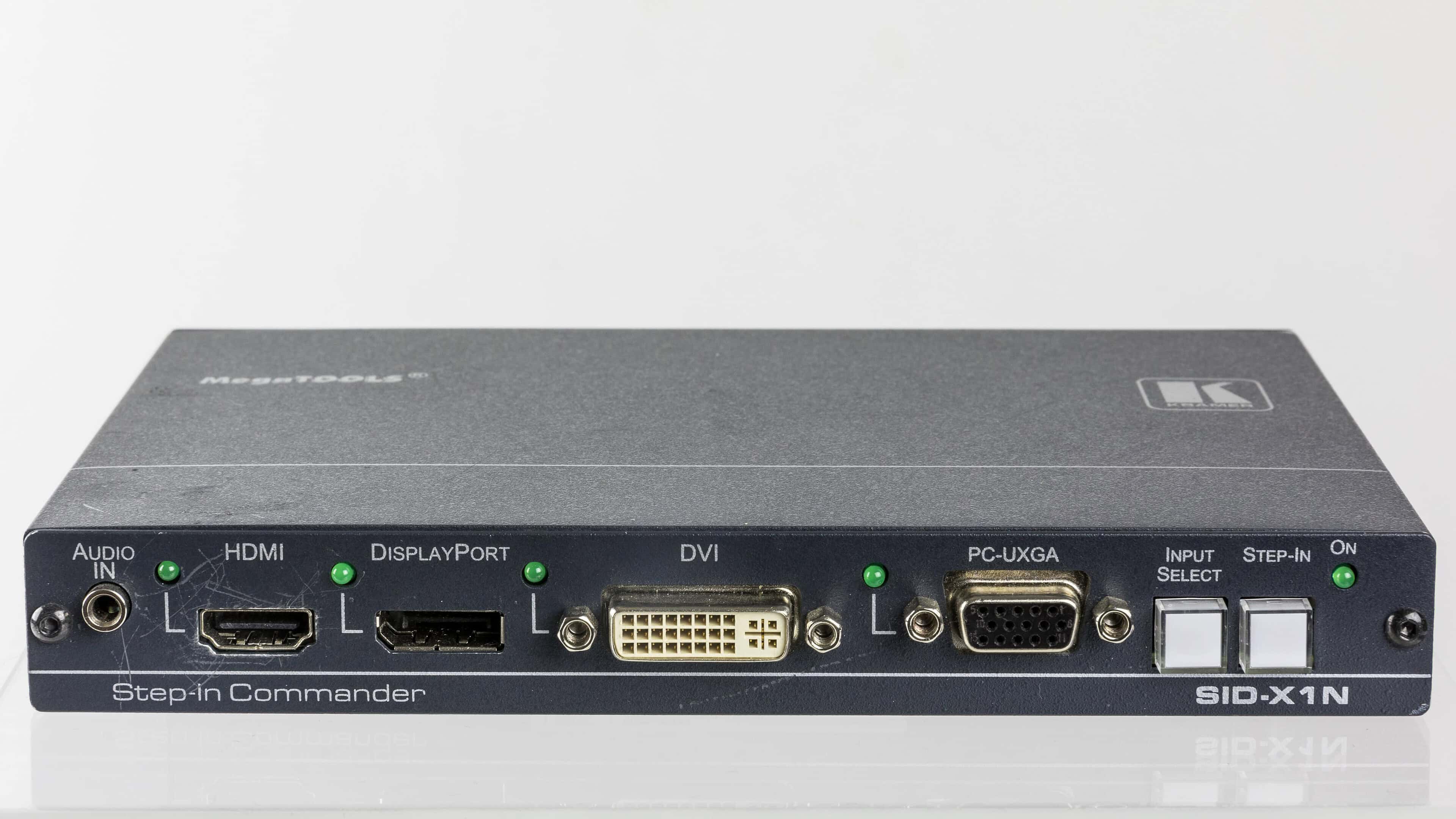
Understanding the differences between video port types is crucial for easy device connectivity. Video ports are what transmit video signals from a device to a display, like a monitor or TV. Common port types include VGA, DVI, HDMI, DisplayPort, and Thunderbolt, each with distinct characteristics and uses. In the past, VGA ports were the standard for video output, but digital standards like HDMI and DisplayPort now offer better quality and features such as audio transmission over the same cable.
DVI ports can transmit both analog and digital signals, bridging old and new technologies. Thunderbolt ports are popular for their high-speed data transfer rates and the ability to connect multiple devices. When choosing a video port, consider factors such as maximum resolution, refresh rate, and audio capabilities based on your specific needs.
Video Port Types
| Image | Port Type | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | VGA | * Stands for Video Graphics Array. * Analog connector. | * Simplest and most widely compatible (older devices). * Low cost. | * Analog signal – Prone to quality loss over longer distances. * Bulky connector. * No audio transmission. | Older monitors, projectors. |
 | DVI | * Stands for Digital Visual Interface. * Digital connector with multiple variations (DVI-D, DVI-I). | * Superior image quality compared to VGA. * Supports digital audio (DVI-I only). | * Multiple variations can cause confusion. * Larger than HDMI. | Older LCD monitors, some modern high-end monitors. |
 | HDMI | * Stands for High-Definition Multimedia Interface. * Most common modern connector. | * Supports high-definition video and audio. * Single cable solution. * Compact connector. | * May require adapters for older devices. | Modern TVs, monitors, laptops, gaming consoles. |
 | DisplayPort | * Developed by VESA. * Primarily used for PCs. | * High resolution and refresh rates. * Supports multiple monitors (daisy-chaining). | * Less common than HDMI on consumer devices. * Requires adapters for other devices. | High-end gaming PCs, monitors. |
 | USB-C | * Multipurpose port for video, data, and power. | * Versatile and future-proof. * Thin and sleek design. | * Requires specific USB-C cable with DisplayPort Alt Mode. | Newer laptops, some monitors. |
 | Thunderbolt | * High-bandwidth interface developed by Intel. | * Fastest video transmission speeds. * Supports multiple high-resolution displays. | * Expensive. * Limited device compatibility. | High-end workstations, professional displays. |
Key Takeaways
- Video ports connect devices to displays and vary in performance and features.
- Digital standards like HDMI and DisplayPort offer enhancements over analog predecessors.
- Choosing the right video port depends on resolution, refresh rate, and special requirements.
Understanding Video Port Types
When connecting monitors, TVs, or projectors, choosing the correct video port is crucial. It impacts display quality and compatibility.
Analog Ports

VGA: Also known as Video Graphics Array, this port sends analog video signals. Developed by IBM, the VGA connector has been standard on computers for many years. The signals it can carry are susceptible to quality loss over longer cables. VGA connectors are commonly found with 15 pins in three rows and are blue.

Composite Video: These ports use RCA connectors, commonly yellow, to transmit analog video signals. They are not as common today but were widely used in early video devices.

Component Video: This type transmits video signals in separate channels for better quality than composite. Component connectors typically use three RCA cables colored red, green, and blue.
Digital Ports

DVI: Created by the Digital Display Working Group, Digital Visual Interface (DVI) ports come in different types. DVI-D carries only digital signals, whereas DVI-I can carry both digital and analog signals. DVI connectors are white and usually have 24 pins plus an additional cross pin for analog signals.

HDMI: High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) is a widely used connector type by manufacturers like Sony and Apple for transmitting both high-definition video and audio. It supports up to 8K resolutions. HDMI cables and ports are compact and support various standards including HDMI 2.1.

DisplayPort: VESA developed the DisplayPort (DP) standard. DisplayPort 1.4 supports high-resolution displays and high refresh rates. Like HDMI, it can carry video and audio signals, but it also supports daisy-chaining multiple monitors.

USB-C and Thunderbolt: These ports, especially Thunderbolt developed by Intel and Apple, can transmit video, audio, data, and power. They are becoming common on laptops and portable devices for their versatility.
Audio-Video Integration
All digital connector types, like HDMI and DisplayPort, carry both audio and video over a single cable. This integration simplifies connections between devices like TVs, monitors, and sound systems. The technology allows for cleaner setups with fewer cables.
Resolution and Quality
The maximum resolution and overall video quality a port can support varies. Modern digital ports like HDMI and DisplayPort support high resolutions including 4K and even 8K, as well as higher refresh rates. These aspects are important for tasks that require detailed images and smooth video playback. Bandwidth, which is the amount of data that can be transmitted at once, is a key factor. Higher bandwidth allows for sending more detailed video signals, resulting in better image quality.
Adaptation, Compatibility and Use Cases
Video ports and connectors serve as critical links between devices and display units, such as monitors and projectors. This section breaks down the different aspects of video connectors, standards, and their practical uses in various scenarios.
Connectors and Adapters
Different devices use various types of connectors to transmit video and audio. Common connectors include HDMI, DVI, VGA, and DisplayPort. Adapters are used when you have incompatible cable and display port types. For example, if a laptop with a USB-C port needs to connect to a monitor with an HDMI input, a USB-C to HDMI adapter will be necessary.
Technology and Standards
Standards for video ports are set by groups like the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA) and the Digital Display Working Group (DDWG). These organizations define the specifications like bandwidth and refresh rates to ensure clear and compatible video transmission. HDMI connections, for example, have evolved to carry more data for higher resolution and are commonly used in consumer electronics.
Practical Applications
Video ports come into play in settings from simple desktop setups to complex video editing stations. A professional might use a multi-port dock with HDMI and SDI (Serial Digital Interface) to connect multiple monitors to a PC. Whereas at home, HDMI cables are often used to connect video game consoles like a Nintendo Wii to televisions.
Entertainment and Gaming
For entertainment, HDMI is the go-to connector for devices like DVD or Blu-ray players and gaming consoles due to its support of high-definition video and audio signals through a single cable. In gaming, adapters might be used to connect older consoles with RCA cables, ensuring they work with newer TVs. Projectors also use various video ports to connect to different sources for large-screen viewing, which is essential for public displays or home cinema setups.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses some common inquiries about video port types, their differences, and their best uses to simplify your technology experience.
What are the differences between HDMI and DisplayPort?
HDMI, or High-Definition Multimedia Interface, is a widely used interface that carries both audio and video signals. It supports various types of video resolutions and is commonly found on TVs, game consoles, and computers. DisplayPort, on the other hand, is often used in computer monitors and professional IT equipment. It has a higher bandwidth than HDMI, which means it can support higher screen refresh rates and resolutions.
How do VGA, HDMI, and DVI ports differ in terms of video quality?
VGA is an older video connection standard that transmits analog video signals and is more susceptible to image degradation over long distances or higher resolutions. HDMI provides a crisp digital video signal and carries audio, which is not supported by VGA. DVI, similar to HDMI, delivers a digital video signal but does not carry audio. Both HDMI and DVI offer sharp images, but HDMI is more versatile due to its audio capability.
Can you list the common types of analog video connectors?
Common types of analog video connectors include the RCA composite video connector, which is often color-coded yellow, and the S-Video connector, which offers a better image quality than composite video. VGA is another analog video connector still in use, mainly for its compatibility with older equipment.
What are the advantages of using a DisplayPort over other video ports?
DisplayPort can daisy-chain multiple monitors with a single connection from a source, support higher resolutions and refresh rates, and provide a direct interface with a PC’s internal graphics processor. These features make DisplayPort a prime choice for high-end computer displays and professional setups.
How does a DVI port compare to other video output options?
DVI ports are typically seen on older computer monitors and projectors. They come in different versions: DVI-A (analog signal), DVI-D (digital signal), and DVI-I (integrated analog and digital signals). DVI-D and HDMI are similar in digital quality, but HDMI’s audio capability and higher resolutions give it a broader application range.
Which video port should be used for the highest quality audio-visual experience?
For the highest quality audio-visual experience, HDMI 2.1 or DisplayPort 2.0 are recommended. HDMI 2.1 supports up to 10K resolution at 120Hz, while DisplayPort 2.0 can handle resolutions up to 16K with a refresh rate of 60Hz. Both support dynamic HDR and have high bandwidth, making them suitable for future-proofing your system for ultra high-definition content.







