AMD Precision Boost Overdrive (PBO) is a technology that enhances the performance of Ryzen CPUs. It builds upon AMD’s standard Precision Boost algorithm, allowing processors to reach higher clock speeds and power levels. PBO tweaks CPU boost limits based on factors like temperature and workload type, potentially improving multithreaded performance.
PBO differs from traditional overclocking methods. It preserves the automated intelligence built into Ryzen processors, including Precision Boost 2. This means users can enjoy improved performance without sacrificing the CPU’s ability to dynamically adjust its clock speeds for optimal efficiency.
Many Ryzen owners wonder if enabling PBO is worthwhile. The answer depends on individual needs and system configurations. PBO can provide noticeable performance gains in certain scenarios, especially for tasks that benefit from increased multithreaded performance.
What Is AMD Precision Boost Overdrive – PBO?
AMD Precision Boost Overdrive (PBO) is a feature found on AMD Ryzen processors that allows for automatic overclocking.1 It works by allowing the processor to boost to higher clock speeds than the default settings, as long as there is thermal and power headroom.
Here’s a breakdown of what PBO does and how it works:
How PBO Works
- Monitoring: PBO constantly monitors various parameters of the CPU, including temperature, current, and voltage.2
- Adjusting Limits: Based on the monitored data, PBO adjusts the power limits (PPT, TDC, EDC) that are typically set in the BIOS.3 This allows the CPU to draw more power and boost to higher clock speeds.4
- Precision Boost 2: PBO works in conjunction with AMD’s Precision Boost 2 algorithm, which is responsible for dynamically adjusting the CPU’s clock speed based on the workload and operating conditions.
- XFR 2: PBO also works with XFR 2 (Extended Frequency Range 2), which allows for even higher clock speeds if the cooling solution is adequate.5
Benefits of PBO
- Increased Performance: PBO can provide a noticeable performance boost in both single-threaded and multi-threaded applications.
- Ease of Use: It’s a simple way to overclock your CPU without having to manually adjust voltage and frequency settings in the BIOS.6
- Adaptive Overclocking: PBO is adaptive, meaning it adjusts the overclocking based on the current workload and operating conditions.7
Things to Keep in Mind
- Cooling: Since PBO allows the CPU to draw more power, it’s important to have a good cooling solution to prevent the CPU from overheating.
- Motherboard: The motherboard’s VRM (Voltage Regulator Module) quality plays a role in how effective PBO can be. A higher-quality VRM can deliver more stable power to the CPU, allowing for higher and more consistent boost clocks.
- Silicon Lottery: The quality of the CPU itself (silicon lottery) can also affect PBO results. Some CPUs may be able to boost higher than others.

Enabling PBO
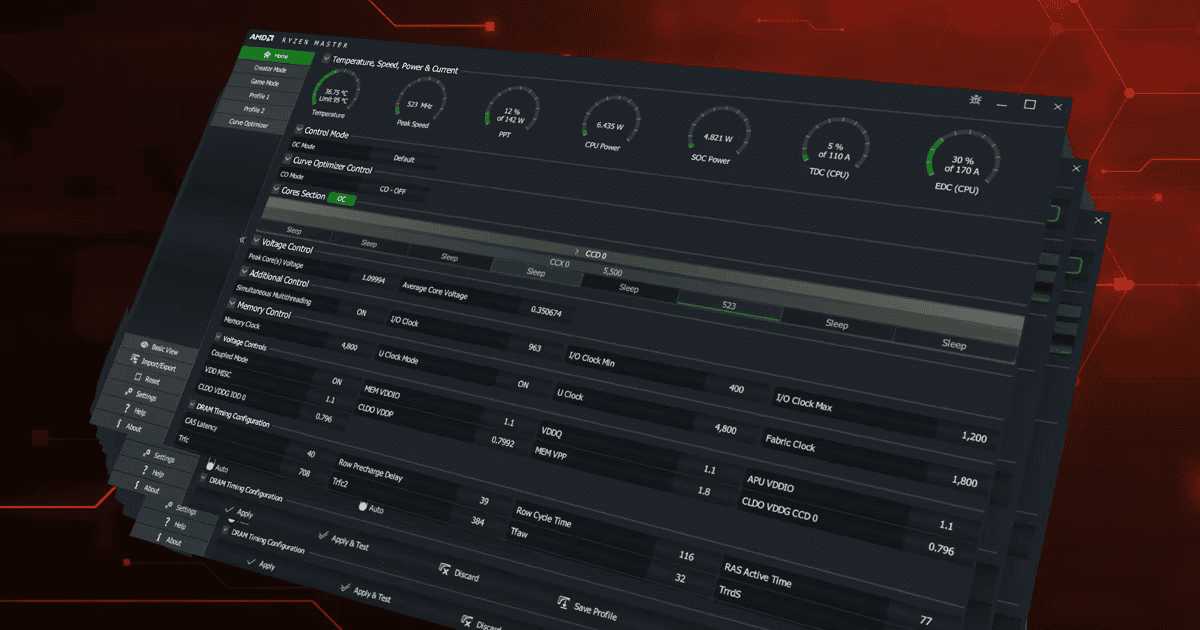
PBO can typically be enabled in the BIOS or through AMD’s Ryzen Master software.8 The specific settings and options may vary depending on the motherboard and CPU.
When To Enable or Disable PBO
| When to Enable PBO | When Not to Enable PBO |
|---|---|
| You want an easy way to increase your CPU performance. | You’re not comfortable with any level of automatic overclocking. |
| You have a good CPU cooler (air or liquid). | You have a basic stock cooler. |
| Your motherboard has a decent VRM (Voltage Regulator Module). | You have a low-end motherboard with a weak VRM. |
| You want to maximize performance in games and applications. | You prioritize stability and low power consumption over maximum performance. |
| You’re comfortable with potentially higher power consumption and temperatures. | You’re concerned about your CPU running too hot or using too much power. |
| You want the CPU to dynamically adjust its performance based on the workload. | You prefer to have full manual control over your CPU’s clock speeds and voltages. |
PBO is a great feature for users who want to get a bit more performance out of their AMD Ryzen CPU without the hassle of manual overclocking. It’s a safe and effective way to boost clock speeds while still maintaining the CPU’s built-in safety features.
Key Takeaways
- PBO enhances Ryzen CPU performance by adjusting boost limits
- It preserves automated CPU intelligence unlike traditional overclocking
- PBO’s effectiveness varies based on individual system setups and workloads
Understanding Precision Boost Overdrive (PBO) and System Requirements
Precision Boost Overdrive (PBO) is an advanced feature for AMD Ryzen processors that enhances CPU performance. It requires specific hardware and configuration to function properly.
The Fundamentals of PBO
PBO is an intelligent boosting algorithm that works alongside AMD’s standard Precision Boost technology. It adjusts CPU limits based on factors like temperature and workload type. PBO aims to improve multithreaded performance while keeping the automated intelligence of Ryzen CPUs intact.
Unlike traditional overclocking, PBO maintains Precision Boost 2 functionality. This allows for on-demand performance adjustments. PBO tweaks power delivery, current, and thermal limits to push the CPU beyond its stock settings.
Users should note that enabling PBO may affect their warranty. AMD’s product warranty and some manufacturer warranties may be voided when using this feature.
Compatible Hardware
PBO is available on select AMD Ryzen processors. These include:
- AMD Ryzen Threadripper CPUs
- AMD Ryzen 5 3000 series
- AMD Ryzen 7 3000 series
- AMD Ryzen 9 3000 series and newer
A compatible motherboard is also necessary to use PBO. Not all motherboards support this feature, so users should check their specifications carefully.
The effectiveness of PBO can vary due to the “silicon lottery” – the natural variation in chip quality. Some CPUs may see more significant performance gains than others.
BIOS Settings and Configuration
Enabling PBO typically requires accessing the motherboard BIOS. The exact location of PBO settings can differ between manufacturers. Common places to find PBO options include:
- Overclocking sections
- AMD CBS (Custom BIOS Settings) menus
- AMD Overclocking menus
Key PBO parameters that can be adjusted:
- PPT (Package Power Tracking)
- TDC (Thermal Design Current)
- EDC (Electrical Design Current)
Users can also use AMD’s Ryzen Master software to configure PBO on compatible systems. This provides a user-friendly interface for adjusting PBO settings without entering the BIOS.
It’s important to monitor temperatures and stability when using PBO. Small, incremental changes are recommended to find the optimal balance between performance and system reliability.







